Welcome to the world of character-driven code organization, where programming and storytelling intertwine to create captivating web experiences. In this material, we will delve into the CSS box model and its components. Understanding the box model is essential for controlling the layout and spacing of your characters (HTML elements) on the digital stage. Let's explore!
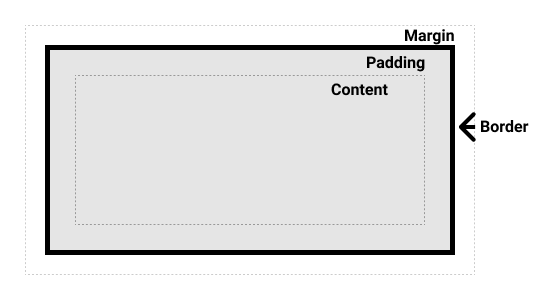
The CSS box model is a fundamental concept that defines how elements are rendered and spaced within a web page. Each HTML element is represented as a rectangular box, consisting of four main components:
-
Content: The actual content of the element, such as text, images, or other nested elements.
-
Padding: The space between the content and the element's border. It provides internal spacing and can be customized using the
paddingproperty. -
Border: The line that surrounds the content and padding. It can be styled using the
borderproperty, defining its width, style, and color. -
Margin: The space outside the element, creating a gap between adjacent elements. It can be adjusted using the
marginproperty.
Understanding these components is crucial for positioning and spacing your characters effectively.
To control the box model components, we can utilize CSS properties. Here's an overview of how to adjust each component:
To define the padding of an element, use the padding property. It accepts values in different units such as pixels (px), percentages (%), or em (relative to the element's font size). For example:
.my-element {
padding: 10px; /* Apply equal padding to all sides */
padding: 10px 20px; /* Apply 10px top/bottom and 20px left/right padding */
padding: 10px 20px 30px 40px; /* Apply 10px top, 20px right, 30px bottom, and 40px left padding */
}To style the border of an element, use the border property. It allows you to specify the border width, style, and color. Here's an example:
.my-element {
border: 2px solid #000; /* Apply a solid black border with a width of 2px */
}To adjust the margin of an element, use the margin property. Like padding, it accepts values in units such as pixels (px), percentages (%), or em. Here's an example:
.my-element {
margin: 10px; /* Apply equal margin to all sides */
margin: 10px auto; /* Apply 10px top/bottom margin and horizontally center the element */
margin: 10px 20px; /* Apply 10px top/bottom margin and 20px left/right margin */
margin: 10px 20px 30px 40px; /* Apply 10px top, 20px right, 30px bottom, and 40px left margin */
}In the character-driven world of code organization, understanding the CSS box model and its components is essential for creating visually appealing web experiences. The box model provides a framework for controlling the layout and spacing of your characters (HTML elements) on the digital stage.
Remember, as software freestyle engineers, we embrace the art of storytelling. By mastering the CSS box model, you gain the ability to position and space your characters effectively, enhancing their presence and impact on the web page.