diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/aspnet-core-webapi/_index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/aspnet-core-webapi/_index.mdx
index 9fb66aa6f..98dbb40a8 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/aspnet-core-webapi/_index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/aspnet-core-webapi/_index.mdx
@@ -143,8 +143,8 @@ export const sections = [
The way in which you call your API depends on the type of application you are developing and the framework you
are using. To learn more, read the relevant application Quickstart:
- - [Single-Page Applications](/docs/quickstart#single-page-app)
- - [Mobile / Native Application](/docs/quickstart#native-mobile-app)
+ - [Single-Page Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/quickstart#single-page-app)
+ - [Mobile / Native Application](https://auth0.com/docs/quickstart#native-mobile-app)
### Get an access token
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/aspnet-core-webapi/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/aspnet-core-webapi/index.mdx
index f189b8a0e..377a72b2b 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/aspnet-core-webapi/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/aspnet-core-webapi/index.mdx
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ System requirements: .NET 6.0 | .NET 7.0 | .NET 8.0
*/}
-**New to Auth0?** Learn [how Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview) and read about [implementing API authentication and authorization](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
+**New to Auth0?** Learn [how Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview) and read about [implementing API authentication and authorization](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
## Configure Auth0 APIs
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ In the [APIs](https://manage.auth0.com/#/apis) section of the Auth0 dashboard, c
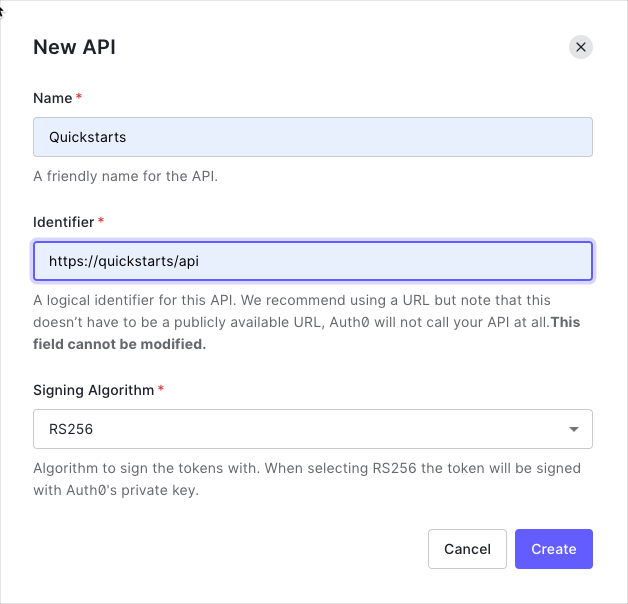
-By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
+By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
### Define permissions
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ This example uses the `read:messages` scope.
This example demonstrates:
* How to check for a JSON Web Token (JWT) in the `Authorization` header of an incoming HTTP request.
-* How to check if the token is valid, using the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see [Validate Access Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
+* How to check if the token is valid, using the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see [Validate Access Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
## Configure the Sample Project
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/django/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/django/index.mdx
index 1d6a9a9d4..f330ae250 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/django/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/django/index.mdx
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ System requirements: Python 3.5 and up | Django 2.2.\* | djangorestframework 3.1
*/}
-**New to Auth0?** Learn [how Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview) and read about [implementing API authentication and authorization](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
+**New to Auth0?** Learn [how Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview) and read about [implementing API authentication and authorization](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
## Configure Auth0 APIs
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ In the [APIs](https://manage.auth0.com/#/apis) section of the Auth0 dashboard, c

-By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
+By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
### Define permissions
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ This example uses the `read:messages` scope.
This example demonstrates:
* How to check for a JSON Web Token (JWT) in the `Authorization` header of an incoming HTTP request.
-* How to check if the token is valid, using the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see [Validate Access Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
+* How to check if the token is valid, using the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see [Validate Access Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
## Setup the Django Application
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/golang/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/golang/index.mdx
index a4375a66c..3b839bd81 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/golang/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/golang/index.mdx
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ System requirements: Go 1.21+
*/}
-**New to Auth0?** Learn [how Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview) and read about [implementing API authentication and authorization](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
+**New to Auth0?** Learn [how Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview) and read about [implementing API authentication and authorization](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
## Configure Auth0 APIs
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ In the [APIs](https://manage.auth0.com/#/apis) section of the Auth0 dashboard, c

-By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
+By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
### Define permissions
@@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ This example uses the `read:messages` scope.
This example demonstrates:
* How to check for a JSON Web Token (JWT) in the `Authorization` header of an incoming HTTP request.
-* How to check if the token is valid, using the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see [Validate Access Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
+* How to check if the token is valid, using the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see [Validate Access Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
## Validate Access Tokens
@@ -185,7 +185,7 @@ func EnsureValidToken() func(next http.Handler) http.Handler {
-By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
+By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
## Protect API Endpoints
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/java-spring-security5/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/java-spring-security5/index.mdx
index efa106285..bd45dc307 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/java-spring-security5/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/java-spring-security5/index.mdx
@@ -16,10 +16,10 @@ System requirements: Java 17
This example demonstrates:
* How to check for a JSON Web Token (JWT) in the `Authorization` header of an incoming HTTP request.
-* How to check if the token is valid, using the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see [Validate Access Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
+* How to check if the token is valid, using the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see [Validate Access Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
-**New to Auth0?** Learn [how Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview) and read about [implementing API authentication and authorization](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
+**New to Auth0?** Learn [how Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview) and read about [implementing API authentication and authorization](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ In the [APIs](https://manage.auth0.com/#/apis) section of the Auth0 dashboard, c

-By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
+By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
### Define permissions
@@ -259,12 +259,12 @@ mvn.cmd spring-boot:run
```
-The sample application will be available at `http://localhost:3010/`. Read about how to test and use your API in the [Using Your API](/docs/quickstart/backend/java-spring-security5/02-using) article.
+The sample application will be available at `http://localhost:3010/`. Read about how to test and use your API in the [Using Your API](https://auth0.com/docs/quickstart/backend/java-spring-security5/02-using) article.
##### What can you do next?
-[Part 2: Using Your API](/docs/quickstart/backend/java-spring-security5/02-using)
+[Part 2: Using Your API](https://auth0.com/docs/quickstart/backend/java-spring-security5/02-using)
[Edit on GitHub](https://github.com/auth0/docs/edit/master/articles/quickstart/backend/java-spring-security5/01-authorization.md)
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/nodejs/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/nodejs/index.mdx
index 11cbbe244..753e27fa5 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/nodejs/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/nodejs/index.mdx
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ System requirements: express-oauth2-jwt-bearer 1.0.0
*/}
-**New to Auth0?** Learn [how Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview) and read about [implementing API authentication and authorization](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
+**New to Auth0?** Learn [how Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview) and read about [implementing API authentication and authorization](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
## Configure Auth0 APIs
@@ -25,10 +25,10 @@ In the [APIs](https://manage.auth0.com/#/apis) section of the Auth0 dashboard, c

-By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
+By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
-We recommend using the default RS256 [signing algorithm](/docs/get-started/applications/signing-algorithms) for your API. If you need to use the HS256 algorithm, see the [HS256 integration sample](https://github.com/auth0-samples/auth0-express-api-samples/tree/master/02-Authorization-HS256).
+We recommend using the default RS256 [signing algorithm](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/applications/signing-algorithms) for your API. If you need to use the HS256 algorithm, see the [HS256 integration sample](https://github.com/auth0-samples/auth0-express-api-samples/tree/master/02-Authorization-HS256).
### Define permissions
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ This example uses the `read:messages` scope.
This example demonstrates:
* How to check for a JSON Web Token (JWT) in the `Authorization` header of an incoming HTTP request.
-* How to check if the token is valid, using the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see [Validate Access Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
+* How to check if the token is valid, using the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see [Validate Access Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
## Validate Access Tokens
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/php/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/php/index.mdx
index 38cd7e477..73f446c22 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/php/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/php/index.mdx
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ System requirements: PHP 7.4+ (8.0 recommended) | Auth0-PHP 8.0 | Composer
*/}
-**New to Auth0?** Learn [how Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview) and read about [implementing API authentication and authorization](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
+**New to Auth0?** Learn [how Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview) and read about [implementing API authentication and authorization](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
## Configure Auth0 APIs
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ In the [APIs](https://manage.auth0.com/#/apis) section of the Auth0 dashboard, c

-By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
+By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
### Define permissions
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ This example uses the `read:messages` scope.
This example demonstrates:
* How to check for a JSON Web Token (JWT) in the `Authorization` header of an incoming HTTP request.
-* How to check if the token is valid, using the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see [Validate Access Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
+* How to check if the token is valid, using the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see [Validate Access Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
## Integrating your PHP Backend API
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/python/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/python/index.mdx
index d13978de8..39a7b869e 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/python/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/python/index.mdx
@@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ System requirements: Python 3.6 and up | Flask 2.0 | Authlib 1.0
*/}
-**New to Auth0?** Learn [how Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview) and read about [implementing API authentication and authorization](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
+**New to Auth0?** Learn [how Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview) and read about [implementing API authentication and authorization](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
## Configure Auth0 APIs
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ In the [APIs](https://manage.auth0.com/#/apis) section of the Auth0 dashboard, c

-By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
+By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
### Define permissions
@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ This example uses the `read:messages` scope.
This example demonstrates:
* How to check for a JSON Web Token (JWT) in the `Authorization` header of an incoming HTTP request.
-* How to check if the token is valid, using the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see [Validate Access Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
+* How to check if the token is valid, using the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see [Validate Access Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
## Validate Access Tokens
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/rails/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/rails/index.mdx
index 7dc3ef908..bad3f24f7 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/rails/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/rails/index.mdx
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ System requirements: Ruby 2.1.8 | Rails 4.2.5
*/}
-**New to Auth0?** Learn [how Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview) and read about [implementing API authentication and authorization](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
+**New to Auth0?** Learn [how Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview) and read about [implementing API authentication and authorization](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
## Configure Auth0 APIs
@@ -23,10 +23,10 @@ In the [APIs](https://manage.auth0.com/#/apis) section of the Auth0 dashboard, c

-By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
+By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
-We recommend using the default RS256 [signing algorithm](/docs/get-started/applications/signing-algorithms) for your API. If you need to use the HS256 algorithm, see the [HS256 integration sample](https://github.com/auth0-samples/auth0-rubyonrails-api-samples/tree/OIDC/02-Authentication-HS256).
+We recommend using the default RS256 [signing algorithm](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/applications/signing-algorithms) for your API. If you need to use the HS256 algorithm, see the [HS256 integration sample](https://github.com/auth0-samples/auth0-rubyonrails-api-samples/tree/OIDC/02-Authentication-HS256).
### Define permissions
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ This example uses the `read:messages` scope.
This example demonstrates:
* How to check for a JSON Web Token (JWT) in the `Authorization` header of an incoming HTTP request.
-* How to check if the token is valid, using the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see [Validate Access Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
+* How to check if the token is valid, using the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see [Validate Access Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
## Validate Access Tokens
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/webapi-owin/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/webapi-owin/index.mdx
index 881c6c52f..f7b270fe3 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/backend/webapi-owin/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/backend/webapi-owin/index.mdx
@@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ System requirements: Microsoft Visual Studio 2015 Update 3 | System.IdentityMode
*/}
-**New to Auth0?** Learn [how Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview) and read about [implementing API authentication and authorization](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
+**New to Auth0?** Learn [how Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview) and read about [implementing API authentication and authorization](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) using the OAuth 2.0 framework.
## Configure Auth0 APIs
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ In the [APIs](https://manage.auth0.com/#/apis) section of the Auth0 dashboard, c

-By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
+By default, your API uses RS256 as the algorithm for signing tokens. Since RS256 uses a private/public keypair, it verifies the tokens against the public key for your Auth0 account. The public key is in the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) format, and can be accessed [here](https://{yourDomain}/.well-known/jwks.json).
### Define permissions
@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ This example uses the `read:messages` scope.
This example demonstrates:
* How to check for a JSON Web Token (JWT) in the `Authorization` header of an incoming HTTP request.
-* How to check if the token is valid, using the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see [Validate Access Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
+* How to check if the token is valid, using the [JSON Web Key Set (JWKS)](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/json-web-tokens/json-web-key-sets) for your Auth0 account. To learn more about validating Access Tokens, see [Validate Access Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
## Configure the Sample Project
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/android-facebook-login/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/android-facebook-login/index.mdx
index 931bbd070..5c9bdbc07 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/android-facebook-login/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/android-facebook-login/index.mdx
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ This tutorial describes how to implement login with the [Facebook SDK](https://d
## Before You Start
* Install and configure the [Facebook Login SDK](https://developers.facebook.com/docs/facebook-login/). You’ll also go through the process of creating a Facebook app in https://developers.facebook.com. **When you finish this step, you should have a mobile app running with Facebook Login integrated.**
-* Configure your Auth0 application in the dashboard to use Facebook Native Sign In. See [Add Facebook Login to Native Apps](/docs/authenticate/identity-providers/social-identity-providers/facebook-native). **When you finish this step, your application will be able to implement Facebook Native Login.**
+* Configure your Auth0 application in the dashboard to use Facebook Native Sign In. See [Add Facebook Login to Native Apps](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/identity-providers/social-identity-providers/facebook-native). **When you finish this step, your application will be able to implement Facebook Native Login.**
## Set up the “Continue with Facebook” button
@@ -254,7 +254,7 @@ If your application does not plan to make use of the Web Authentication module p
```
-However, if you do plan to support Web Authentication, head over [here](/docs/libraries/auth0-android#authentication-via-universal-login) to learn how to declare the Manifest Placeholders.
+However, if you do plan to support Web Authentication, head over [here](https://auth0.com/docs/libraries/auth0-android#authentication-via-universal-login) to learn how to declare the Manifest Placeholders.
### Exchange the received data for Auth0 tokens
@@ -325,7 +325,7 @@ private void exchangeTokens(@NonNull String sessionToken, @NonNull String userPr
It's a good practice to keep all the values that you know won't change as constants at the top of the class. The sample makes use of constants for the subject token type, the Facebook permissions, and the Auth0 scopes.
-You can read more about Auth0 scopes in the dedicated [article](/docs/get-started/apis/scopes/openid-connect-scopes).
+You can read more about Auth0 scopes in the dedicated [article](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/apis/scopes/openid-connect-scopes).
Now that every step is defined in its own method, it's time to put everything together inside the `performLogin` method.
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/device/_index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/device/_index.mdx
index 10e34a152..1fe5f70af 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/device/_index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/device/_index.mdx
@@ -324,7 +324,7 @@ export const sections = [
application requested the `openid` scope) or the API that was specified by the `audience`
parameter. If you are calling your own API, your device application must verify the access token before using it.
- ID tokens contain user information that must be [decoded and extracted](/docs/secure/tokens/id-tokens#id-token-payload). The Authentication API
+ ID tokens contain user information that must be [decoded and extracted](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/id-tokens#id-token-payload). The Authentication API
only returns an `id_token` if your device application requested the `openid` scope.
Refresh tokens are used to obtain a new access token or
@@ -480,8 +480,8 @@ export const sections = [
- Support Server Name Indication (SNI)
- Be a Native Application
- - Have the [Authentication Method](/docs/secure/application-credentials#application-authentication-methods) set to **None**
- - Be [OIDC-conformant](/docs/get-started/applications/application-settings#oauth)
+ - Have the [Authentication Method](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/application-credentials#application-authentication-methods) set to **None**
+ - Be [OIDC-conformant](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/applications/application-settings#oauth)
- Not be created through Dynamic Client Registration
In addition, the Device Authorization Flow does not allow:
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/device/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/device/index.mdx
index 51f5eadbd..7434f837d 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/device/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/device/index.mdx
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ This tutorial demonstrates how to call your API from an input-constrained device
[View on Github](https://github.com/undefined/undefined/tree/master/01-Login) */}
-This tutorial will help you call your own API from an input-constrained device using the Device Authorization Flow. If you want to learn how the flow works and why you should use it, see [Device Authorization Flow](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/device-authorization-flow).
+This tutorial will help you call your own API from an input-constrained device using the Device Authorization Flow. If you want to learn how the flow works and why you should use it, see [Device Authorization Flow](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/device-authorization-flow).
Auth0 makes it easy for your app to implement the Device Authorization flow using:
@@ -29,18 +29,18 @@ Auth0 makes it easy for your app to implement the Device Authorization flow usin
**Before beginning this tutorial:**
* Check [limitations](#limitations) to be sure the Device Authorization flow is suitable for your implementation.
-* [Register the Application with Auth0](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview/create-applications/native-apps).
+* [Register the Application with Auth0](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview/create-applications/native-apps).
+ Select an **Application Type** of **Native**.
+ If necessary, set **Allowed Web Origins**. You can use this to allow localhost as an origin for local development, or to set an allowed origin for specific TV software with architecture subject to CORS (eg: HTML5 + JS). Most applications will not use this setting.
+ Ensure that the **OIDC Conformant** toggle is enabled. This setting is in the [Dashboard](https://manage.auth0.com/#) under **Application Settings > Advanced > OAuth**.
- + Make sure the Application's [**Grant Types**](/docs/get-started/applications/update-grant-types) include **Device Code**. This is also in the [Dashboard](https://manage.auth0.com/#), under **Application Settings > Advanced > Grant Types**.
- + If you want your Application to be able to use [Refresh Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens/refresh-tokens), make sure the Application's [**Grant Types**](/docs/get-started/applications/update-grant-types) include **Refresh Token**.
-* Set up and enable at least one connection for the Application: [Database connections](/docs/get-started/applications/set-up-database-connections), [Social connections](https://marketplace.auth0.com/features/social-connections)
-* [Register your API with Auth0](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api/part-2#create-the-api)
+ + Make sure the Application's [**Grant Types**](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/applications/update-grant-types) include **Device Code**. This is also in the [Dashboard](https://manage.auth0.com/#), under **Application Settings > Advanced > Grant Types**.
+ + If you want your Application to be able to use [Refresh Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/refresh-tokens), make sure the Application's [**Grant Types**](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/applications/update-grant-types) include **Refresh Token**.
+* Set up and enable at least one connection for the Application: [Database connections](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/applications/set-up-database-connections), [Social connections](https://marketplace.auth0.com/features/social-connections)
+* [Register your API with Auth0](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api/part-2#create-the-api)
- + If you want your API to receive [Refresh Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens/refresh-tokens) to allow it to obtain new tokens when the previous ones expire, enable **Allow Offline Access**.
-* [Configure Device User Code Settings](/docs/get-started/tenant-settings/configure-device-user-code-settings) to define the character set, format, and length of your randomly-generated user code.
+ + If you want your API to receive [Refresh Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/refresh-tokens) to allow it to obtain new tokens when the previous ones expire, enable **Allow Offline Access**.
+* [Configure Device User Code Settings](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/tenant-settings/configure-device-user-code-settings) to define the character set, format, and length of your randomly-generated user code.
## Steps
@@ -280,7 +280,7 @@ If all goes well, you'll receive an HTTP 200 response with a payload containing
* `interval` indicates the interval (in seconds) at which the app should poll the token URL to request a token.
-You can [configure the character set, format, and length of your randomly-generated user code](/docs/get-started/tenant-settings/configure-device-user-code-settings) in your tenant settings.
+You can [configure the character set, format, and length of your randomly-generated user code](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/tenant-settings/configure-device-user-code-settings) in your tenant settings.
To prevent brute force attacks, we enforce the following limits on `user_code`:
@@ -591,7 +591,7 @@ This can occur for a variety of reasons, including:
* the user refused to authorize the device
* the authorization server denied the transaction
-* a configured [Rule](/docs/customize/rules) denied access
+* a configured [Rule](https://auth0.com/docs/customize/rules) denied access
## User Authorization
@@ -635,14 +635,14 @@ Once the user has successfully authorized the device, you'll receive an `HTTP 20
```
-You should validate your tokens before saving them. To learn how, see [Validate Access Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens) and [Validate ID Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens/id-tokens/validate-id-tokens).
+You should validate your tokens before saving them. To learn how, see [Validate Access Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens) and [Validate ID Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/id-tokens/validate-id-tokens).
-[Access Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens) are used to call the [Auth0 Authentication API's `/userinfo` endpoint](https://auth0.com/docs/api/authentication#get-user-info) or another API. You will be able to use the Access Token to call `/userinfo` only if you included the `openid` scope. If you are calling your own API, the first thing your API will need to do is [verify the Access Token](/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
+[Access Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens) are used to call the [Auth0 Authentication API's `/userinfo` endpoint](https://auth0.com/docs/api/authentication#get-user-info) or another API. You will be able to use the Access Token to call `/userinfo` only if you included the `openid` scope. If you are calling your own API, the first thing your API will need to do is [verify the Access Token](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens).
-[ID Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens/id-tokens) contain user information that must be [decoded and extracted](/docs/secure/tokens/id-tokens#id-token-payload). The `id_token` will only be present in the response if you included the `openid` scope.
+[ID Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/id-tokens) contain user information that must be [decoded and extracted](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/id-tokens#id-token-payload). The `id_token` will only be present in the response if you included the `openid` scope.
-[Refresh Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens/refresh-tokens) are used to obtain a new Access Token or ID Token after the previous one has expired. The `refresh_token` will only be present in the response if you included the `offline_access` scope and enabled **Allow Offline Access** for your API in the Dashboard.
+[Refresh Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/refresh-tokens) are used to obtain a new Access Token or ID Token after the previous one has expired. The `refresh_token` will only be present in the response if you included the `offline_access` scope and enabled **Allow Offline Access** for your API in the Dashboard.
Refresh Tokens must be stored securely since they allow a user to remain authenticated essentially forever.
@@ -842,7 +842,7 @@ dataTask.resume()
## Refresh Tokens
-You have already received a [Refresh Token](/docs/secure/tokens/refresh-tokens) if you've been following this tutorial and completed the following:
+You have already received a [Refresh Token](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/refresh-tokens) if you've been following this tutorial and completed the following:
* configured your API to allow offline access
* included the `offline_access` scope when you initiated the authentication request through the [authorize](https://auth0.com/docs/api/authentication#authorize-application) endpoint
@@ -1096,14 +1096,14 @@ If all goes well, you'll receive an `HTTP 200` response with a payload containin
```
-You should validate your tokens before saving them. To learn how, see [Validate Access Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens) and [Validate ID Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens/id-tokens/validate-id-tokens).
+You should validate your tokens before saving them. To learn how, see [Validate Access Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/access-tokens/validate-access-tokens) and [Validate ID Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens/id-tokens/validate-id-tokens).
## Sample Use Cases
### Detect Device Authorization Flow Use
-You can use [Rules](/docs/customize/rules) to detect whether the current transaction is using the Device Authorization Flow. To do so, check the `context` object's `protocol` property:
+You can use [Rules](https://auth0.com/docs/customize/rules) to detect whether the current transaction is using the Device Authorization Flow. To do so, check the `context` object's `protocol` property:
```javascript lines
function (user, context, callback) {
@@ -1123,7 +1123,7 @@ function (user, context, callback) {
# Troubleshooting
-[Tenant logs](/docs/deploy-monitor/logs) are created for any interaction that takes place and can be used to troubleshoot issues.
+[Tenant logs](https://auth0.com/docs/deploy-monitor/logs) are created for any interaction that takes place and can be used to troubleshoot issues.
## Error codes
@@ -1168,23 +1168,23 @@ function (user, context, callback) {
To use the Device Authorization Flow, devices must:
* Support Server Name Indication (SNI)
-* Have an [Auth0 application type](/docs/get-started/applications) of **Native**
-* Have the [**Token Endpoint Authentication Method**](/docs/get-started/applications/application-settings) set to **None**
-* Be [OIDC-conformant](/docs/get-started/applications/application-settings#oauth)
-* Not be created through [Dynamic Client Registration](/docs/get-started/applications/dynamic-client-registration)
+* Have an [Auth0 application type](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/applications) of **Native**
+* Have the [**Token Endpoint Authentication Method**](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/applications/application-settings) set to **None**
+* Be [OIDC-conformant](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/applications/application-settings#oauth)
+* Not be created through [Dynamic Client Registration](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/applications/dynamic-client-registration)
In addition, the Device Authorization Flow does not allow:
-* [Social Connections](/docs/authenticate/identity-providers) using [Auth0 developer keys](/docs/authenticate/identity-providers/social-identity-providers/devkeys) unless you are using new [New Universal Login Experience](/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login/universal-login-vs-classic-login/universal-experience).
+* [Social Connections](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/identity-providers) using [Auth0 developer keys](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/identity-providers/social-identity-providers/devkeys) unless you are using new [New Universal Login Experience](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login/universal-login-vs-classic-login/universal-experience).
* Query string parameters to be accessed from hosted login page or rules
We support the full [Draft 15](https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-oauth-device-flow-15), except for confidential Clients.
## Keep reading
-* [The OAuth 2.0 protocol](/docs/authenticate/protocols/oauth)
-* [The OpenID Connect protocol](/docs/authenticate/protocols/openid-connect-protocol)
-* [Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens)
-* [Tenant Logs for Devices](/docs/deploy-monitor/logs)
+* [The OAuth 2.0 protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/protocols/oauth)
+* [The OpenID Connect protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/protocols/openid-connect-protocol)
+* [Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens)
+* [Tenant Logs for Devices](https://auth0.com/docs/deploy-monitor/logs)
[Edit on GitHub](https://github.com/auth0/docs/edit/master/articles/quickstart/native/device/01-login.md)
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/flutter/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/flutter/index.mdx
index e37432880..79618c907 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/flutter/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/flutter/index.mdx
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ This quickstart assumes you already have a [Flutter](https://flutter.dev/) app u
You should also be familiar with the [Flutter command line tool](https://docs.flutter.dev/reference/flutter-cli).
-Finally, you will need a **Native** Auth0 application. If you don’t have a Native Auth0 application already, [create one](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview/create-applications/native-apps) before continuing. Avoid using other application types, as they have different configurations and may cause errors.
+Finally, you will need a **Native** Auth0 application. If you don’t have a Native Auth0 application already, [create one](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview/create-applications/native-apps) before continuing. Avoid using other application types, as they have different configurations and may cause errors.
### Configure the callback and logout URLs
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ The callback and logout URLs are the URLs that Auth0 invokes to redirect back to
If the callback and logout URLs are not set, users will be unable to log in and out of the app and will get an error.
-Go to the [settings page](https://manage.auth0.com/#/applications/{yourClientId}/settings) of your Auth0 application and add the following URLs to **Allowed Callback URLs** and **Allowed Logout URLs**, depending on the platform of your app. If you have a [custom domain](/docs/customize/custom-domains), use this instead of the Auth0 domain from the settings page.
+Go to the [settings page](https://manage.auth0.com/#/applications/{yourClientId}/settings) of your Auth0 application and add the following URLs to **Allowed Callback URLs** and **Allowed Logout URLs**, depending on the platform of your app. If you have a [custom domain](https://auth0.com/docs/customize/custom-domains), use this instead of the Auth0 domain from the settings page.
On Android, the value of the `SCHEME` placeholder can be `https` or some other custom scheme. Whenever possible, Auth0 recommends using [Android App Links](https://auth0.com/docs/applications/enable-android-app-links) with `https` as a secure way to link directly to content within your app. Custom URL schemes can be subject to [client impersonation attacks](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc8252#section-8.6).
@@ -178,7 +178,7 @@ export const codeExample2 = `webcredentials:{yourDomain}`;
-If you have a [custom domain](/docs/customize/custom-domains), use this instead of the Auth0 domain from the settings page.
+If you have a [custom domain](https://auth0.com/docs/customize/custom-domains), use this instead of the Auth0 domain from the settings page.
For the associated domain to work, your app must be signed with your team certificate **even when building for the iOS simulator**. Make sure you are using the Apple Team whose Team ID is configured in the settings page of your Auth0 application.
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-angular/_index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-angular/_index.mdx
index b3040c151..c35a7e356 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-angular/_index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-angular/_index.mdx
@@ -152,7 +152,7 @@ export const sections = [
To persist authentication after closing and reopening the application, you may want to set
`cacheLocation` to `localstorage` when configuring the SDK, but please be aware of
[the risks of
- storing tokens in localstorage](/docs/libraries/auth0-single-page-app-sdk#change-storage-options). Also, localstorage should be treated as **transient** in
+ storing tokens in localstorage](https://auth0.com/docs/libraries/auth0-single-page-app-sdk#change-storage-options). Also, localstorage should be treated as **transient** in
Capacitor app as the data might be recovered unexpectedly in certain circumstances. Please read the [guidance on storage in the Capacitor docs](https://capacitorjs.com/docs/guides/storage#why-cant-i-just-use-localstorage-or-indexeddb).
Additionally, the SDK has the ability to [use a custom cache implementation](https://github.com/auth0/auth0-spa-js/blob/master/EXAMPLES.md#creating-a-custom-cache) to store tokens, if
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-angular/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-angular/index.mdx
index 288bf983c..68a8b563e 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-angular/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-angular/index.mdx
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ This quickstart assumes you already have an [Ionic](https://ionicframework.com/)
You should also be familiar with the [Capacitor development workflow](https://capacitorjs.com/docs/basics/workflow).
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-react/_index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-react/_index.mdx
index 8ac62d4c3..c7a85bb53 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-react/_index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-react/_index.mdx
@@ -153,7 +153,7 @@ export const sections = [
To persist authentication after closing and reopening the application, you may want to set
`cacheLocation` to `localstorage` when configuring the SDK, but please be aware of
[the risks of
- storing tokens in localstorage](/docs/libraries/auth0-single-page-app-sdk#change-storage-options). Also, localstorage should be treated as **transient** in
+ storing tokens in localstorage](https://auth0.com/docs/libraries/auth0-single-page-app-sdk#change-storage-options). Also, localstorage should be treated as **transient** in
Capacitor app as the data might be recovered unexpectedly in certain circumstances. Please read the [guidance on storage in the Capacitor docs](https://capacitorjs.com/docs/guides/storage#why-cant-i-just-use-localstorage-or-indexeddb).
Additionally, the SDK has the ability to [use a custom cache implementation](https://github.com/auth0/auth0-spa-js/blob/master/EXAMPLES.md#creating-a-custom-cache) to store tokens, if
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-react/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-react/index.mdx
index db7fa7149..0d0e408d3 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-react/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-react/index.mdx
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ This quickstart assumes you already have an [Ionic](https://ionicframework.com/)
You should also be familiar with the [Capacitor development workflow](https://capacitorjs.com/docs/basics/workflow).
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-vue/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-vue/index.mdx
index d34ab2bde..bd962340d 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-vue/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/ionic-vue/index.mdx
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ This quickstart assumes you already have an [Ionic](https://ionicframework.com/)
You should also be familiar with the [Capacitor development workflow](https://capacitorjs.com/docs/basics/workflow).
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/maui/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/maui/index.mdx
index 29c5292ee..f9731ba3e 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/maui/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/maui/index.mdx
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ The MAUI SDK supports Android, iOS, macOS, and Windows. Continue reading for pla
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/net-android-ios/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/net-android-ios/index.mdx
index 42bb13b8e..fcec1e24e 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/net-android-ios/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/net-android-ios/index.mdx
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ This quickstart focusses on .NET Android and iOS, as they are the next generatio
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/react-native-expo/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/react-native-expo/index.mdx
index 866beb06a..a36efebb6 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/react-native-expo/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/react-native-expo/index.mdx
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ This SDK is not compatible with "Expo Go" app. It is compatible only with Custom
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ npm install react-native-auth0 --save
-The first step in adding authentication to your application is to provide a way for your users to log in. The fastest, most secure, and most feature-rich way to do this with Auth0 is to use the hosted [login page](/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login).
+The first step in adding authentication to your application is to provide a way for your users to log in. The fastest, most secure, and most feature-rich way to do this with Auth0 is to use the hosted [login page](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login).
@@ -161,7 +161,7 @@ The callback and logout URLs are the URLs that Auth0 invokes to redirect back to
If the callback and logout URLs are not set, users will be unable to log in and out of the application and will get an error.
-Go to the settings page of your [Auth0 application](https://manage.auth0.com/#/applications/{yourClientId}/settings) and add the corresponding URL to **Allowed Callback URLs** and **Allowed Logout URLs**, according to the platform of your application. If you are using a [custom domain](/docs/customize/custom-domains), use the value of your custom domain instead of the Auth0 domain from the settings page.
+Go to the settings page of your [Auth0 application](https://manage.auth0.com/#/applications/{yourClientId}/settings) and add the corresponding URL to **Allowed Callback URLs** and **Allowed Logout URLs**, according to the platform of your application. If you are using a [custom domain](https://auth0.com/docs/customize/custom-domains), use the value of your custom domain instead of the Auth0 domain from the settings page.
#### iOS
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/react-native/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/react-native/index.mdx
index d22684cb9..7450c49fe 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/react-native/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/react-native/index.mdx
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ System requirements: React Native 0.62.2 | NodeJS 10.16
This Quickstart is for the React Native framework. To integrate Auth0 into your Expo application, please refer to the [Expo Quickstart](https://auth0.com/docs/quickstart/native/react-native-expo/interactive)
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
@@ -98,7 +98,7 @@ pod install
-First, you must provide a way for your users to log in. We recommend using the Auth0 hosted [login page](/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login).
+First, you must provide a way for your users to log in. We recommend using the Auth0 hosted [login page](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login).

@@ -217,7 +217,7 @@ The callback and logout URLs are the URLs that Auth0 invokes to redirect back to
If the callback and logout URLs are not set, users will be unable to log in and out of the application and will get an error.
-Go to the settings page of your [Auth0 application](https://manage.auth0.com/#/applications/{yourClientId}/settings) and add the corresponding URL to **Allowed Callback URLs** and **Allowed Logout URLs**, according to the platform of your application. If you are using a [custom domain](/docs/customize/custom-domains), use the value of your custom domain instead of the Auth0 domain from the settings page.
+Go to the settings page of your [Auth0 application](https://manage.auth0.com/#/applications/{yourClientId}/settings) and add the corresponding URL to **Allowed Callback URLs** and **Allowed Logout URLs**, according to the platform of your application. If you are using a [custom domain](https://auth0.com/docs/customize/custom-domains), use the value of your custom domain instead of the Auth0 domain from the settings page.
#### iOS
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/windows-uwp-csharp/_index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/windows-uwp-csharp/_index.mdx
index 864b41e52..711b1b4ea 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/windows-uwp-csharp/_index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/windows-uwp-csharp/_index.mdx
@@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ export const sections = [
- Auth0.OidcClient.UWP 4.0.0
- **New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
+ **New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
### Get Your Application Keys
@@ -153,7 +153,7 @@ export const sections = [
 - This loads the Auth0 login page into a web view. You can learn how to customize the login page at [this document](/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login#simple-customization).
+ This loads the Auth0 login page into a web view. You can learn how to customize the login page at [this document](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login#simple-customization).
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/windows-uwp-csharp/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/windows-uwp-csharp/index.mdx
index 5a726240d..902aa7941 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/windows-uwp-csharp/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/windows-uwp-csharp/index.mdx
@@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ System requirements: Microsoft Visual Studio 2017 | Windows 10 SDK (10.0.10586.0
*/}
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
@@ -102,7 +102,7 @@ var loginResult = await client.LoginAsync();
-This will load the Auth0 login page into a web view. You can learn how to customize the login page in [this document](/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login#simple-customization).
+This will load the Auth0 login page into a web view. You can learn how to customize the login page in [this document](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login#simple-customization).
## Handle Authentication Tokens
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/wpf-winforms/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/wpf-winforms/index.mdx
index b646aaaf1..eafb964a8 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/wpf-winforms/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/wpf-winforms/index.mdx
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ System requirements: Microsoft Visual Studio 2022 | .NET Framework 4.6.2 | .NET
*/}
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
@@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ If you are following along with the sample project you downloaded from the top o
### Install Dependencies
-The `Auth0.OidcClient.WPF` or `Auth0.OidcClient.WinForms` NuGet packages helps you authenticate users with any [Auth0 supported identity provider](/docs/authenticate/identity-providers).
+The `Auth0.OidcClient.WPF` or `Auth0.OidcClient.WinForms` NuGet packages helps you authenticate users with any [Auth0 supported identity provider](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/identity-providers).
Use the NuGet Package Manager (Tools -> Library Package Manager -> Package Manager Console) to install the `Auth0.OidcClient.WPF` or `Auth0.OidcClient.WinForms` package, depending on whether you are building a WPF or Windows Forms application:
@@ -98,7 +98,7 @@ var loginResult = await client.LoginAsync();
-This will load the Auth0 login page into a web view. You can learn how to customize the login page in [this document](/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login#simple-customization).
+This will load the Auth0 login page into a web view. You can learn how to customize the login page in [this document](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login#simple-customization).
## Handle Authentication Tokens
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/xamarin/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/xamarin/index.mdx
index 8e2ae56b7..66c3b726e 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/xamarin/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/xamarin/index.mdx
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ This quickstart focusses on .NET Android and iOS, as they are the next generatio
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/spa/flutter/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/spa/flutter/index.mdx
index e2baec73d..a7ad146c8 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/spa/flutter/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/spa/flutter/index.mdx
@@ -119,7 +119,7 @@ export const sections = [
- [Universal Login](/docs/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login) is
+ [Universal Login](https://auth0.com/docs/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login) is
the easiest way to set up authentication in your application. We recommend using it for the best experience, best
security, and the fullest array of features.
@@ -128,7 +128,7 @@ export const sections = [
You will normally need to specify the `redirectUrl` parameter to
- `loginWithRedirect`. Omitting this will cause Auth0 to use the [default login route](/docs/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login/configure-default-login-routes), which is not configured by default.
+ `loginWithRedirect`. Omitting this will cause Auth0 to use the [default login route](https://auth0.com/docs/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login/configure-default-login-routes), which is not configured by default.
When a user logs in, they are redirected back to your application. You are then able to access the ID and access
@@ -160,11 +160,11 @@ export const sections = [
To log users out, redirect them to the Auth0 logout endpoint to clear their login session by calling the Auth0
Flutter SDK `logout()`. [Read
- more about logging out of Auth0](/docs/docs/authenticate/login/logout).
+ more about logging out of Auth0](https://auth0.com/docs/docs/authenticate/login/logout).
You will normally want to specify `returnToUrl` when calling `logout`, otherwise
- Auth0 [will default to the first URL in the Allowed Logout URLs list](/docs/docs/authenticate/login/logout/redirect-users-after-logout).
+ Auth0 [will default to the first URL in the Allowed Logout URLs list](https://auth0.com/docs/docs/authenticate/login/logout/redirect-users-after-logout).
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-core-blazor-server/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-core-blazor-server/index.mdx
index fcd0f6177..cd62912b2 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-core-blazor-server/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-core-blazor-server/index.mdx
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ If you are following along with the sample project you downloaded from the top o
## Integrate Auth0
-[Universal Login](/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login) is the easiest way to set up authentication in your application. We recommend using it for the best experience, security, and the most complete array of features. This guide uses Universal Login to provide a way for your users to log in to your Blazor Server application.
+[Universal Login](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login) is the easiest way to set up authentication in your application. We recommend using it for the best experience, security, and the most complete array of features. This guide uses Universal Login to provide a way for your users to log in to your Blazor Server application.
### Install dependencies
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-core/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-core/index.mdx
index eddcbc9f9..d5f6ca20f 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-core/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-core/index.mdx
@@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ If you are following along with the sample project you downloaded from the top o
## Integrate Auth0
-[Universal Login](/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login) is the easiest way to set up authentication in your application. We recommend using it for the best experience, best security and the fullest array of features. This guide will use it to provide a way for your users to log in to your ASP.NET Core application.
+[Universal Login](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login) is the easiest way to set up authentication in your application. We recommend using it for the best experience, best security and the fullest array of features. This guide will use it to provide a way for your users to log in to your ASP.NET Core application.
### Install dependencies
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-owin/_index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-owin/_index.mdx
index 715e4167a..16c432ea6 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-owin/_index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-owin/_index.mdx
@@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ export const sections = [
For the SDK to function properly, set the following properties in `Web.config`:
- - `auth0:Domain`: The domain of your Auth0 tenant. You can find this in the Auth0 Dashboard under your application's **Settings **in the Domain field. If you are using a [custom domain](/docs/customize/custom-domains), set this to the value of your custom domain instead.
+ - `auth0:Domain`: The domain of your Auth0 tenant. You can find this in the Auth0 Dashboard under your application's **Settings **in the Domain field. If you are using a [custom domain](https://auth0.com/docs/customize/custom-domains), set this to the value of your custom domain instead.
- `auth0:ClientId`: The ID of the Auth0 application you created in Auth0 Dashboard. You can find this in the Auth0 Dashboard under your application's **Settings **in the Client ID field.
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-owin/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-owin/index.mdx
index ea654a3ea..f33aafdbe 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-owin/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-owin/index.mdx
@@ -169,7 +169,7 @@ public void Configuration(IAppBuilder app)
It is essential that you register both the cookie middleware and the OpenID Connect middleware, as they are required (in that order) for the authentication to work. The OpenID Connect middleware will handle the authentication with Auth0. Once the user has authenticated, their identity will be stored in the cookie middleware.
-In the code snippet above, note that the `AuthenticationType` is set to **Auth0**. This will be used in the next section to challenge the OpenID Connect middleware and start the authentication flow. Also note code in the `RedirectToIdentityProvider` notification event which constructs the correct [logout URL](/docs/authenticate/login/logout).
+In the code snippet above, note that the `AuthenticationType` is set to **Auth0**. This will be used in the next section to challenge the OpenID Connect middleware and start the authentication flow. Also note code in the `RedirectToIdentityProvider` notification event which constructs the correct [logout URL](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/logout).
## Add login to your ASP.NET OWIN application
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/django/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/django/index.mdx
index ad45b77fc..67a7ffc53 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/django/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/django/index.mdx
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ System requirements: Python 3 | Authlib 1.0 | Django 4.0
*/}
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/golang/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/golang/index.mdx
index 24296c24c..c8c95b589 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/golang/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/golang/index.mdx
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ System requirements: Go 1.21+
*/}
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
@@ -478,12 +478,12 @@ func Handler(ctx *gin.Context) {
-For information about the userinfo hash, see [User Profile](/docs/manage-users/user-accounts/user-profiles).
+For information about the userinfo hash, see [User Profile](https://auth0.com/docs/manage-users/user-accounts/user-profiles).
## Logging Out
To log the user out, clear the data from the session and redirect the user to the Auth0 logout endpoint. You can find
-more information about this in the [logout documentation](/docs/authenticate/login/logout).
+more information about this in the [logout documentation](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/logout).
Create a file called `logout.go` in the folder `web/app/logout/logout.go`, and add the function `Handler` to redirect
the user to Auth0's logout endpoint.
@@ -534,7 +534,7 @@ func Handler(ctx *gin.Context) {
-The redirect URL needs to be in the list of Allowed Logout URLs in the settings section of the application, For more information, see [Redirect Users After Logout](/docs/authenticate/login/logout/guides/redirect-users-after-logout).
+The redirect URL needs to be in the list of Allowed Logout URLs in the settings section of the application, For more information, see [Redirect Users After Logout](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/logout/guides/redirect-users-after-logout).
Create a file called `user.js` in the folder `web/static/js`, and add the code to remove the cookie from a logged-in
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java-ee/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java-ee/index.mdx
index 4e07d03af..ef9e7a3f3 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java-ee/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java-ee/index.mdx
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ System requirements: Java 11
*/}
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java-spring-boot/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java-spring-boot/index.mdx
index ddebdd3f6..1ac206893 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java-spring-boot/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java-spring-boot/index.mdx
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ This tutorial uses [Spring MVC](https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/sprin
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java/index.mdx
index 30d06fb17..d4bdef338 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java/index.mdx
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ System requirements: Java 8 | Gradle 3.3 and up
*/}
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
@@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ If you are following along with the sample project you downloaded from the top o
To integrate your Java application with Auth0, add the following dependencies:
* **javax.servlet-api**: is the library that allows you to create Java Servlets. You then need to add a Server dependency like Tomcat or Gretty, which one is up to you. Check our sample code for more information.
-* **auth0-java-mvc-commons**: is the [Java library](https://github.com/auth0/auth0-java-mvc-common) that allows you to use Auth0 with Java for server-side MVC web apps. It generates the Authorize URL that you need to call in order to authenticate and validates the result received on the way back to finally obtain the [Auth0 Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens) that identify the user.
+* **auth0-java-mvc-commons**: is the [Java library](https://github.com/auth0/auth0-java-mvc-common) that allows you to use Auth0 with Java for server-side MVC web apps. It generates the Authorize URL that you need to call in order to authenticate and validates the result received on the way back to finally obtain the [Auth0 Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens) that identify the user.
If you are using Gradle, add them to your `build.gradle`:
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/php/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/php/index.mdx
index 3b4e551c1..c3b4cbb84 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/php/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/php/index.mdx
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ System requirements: PHP 7.4+ (8.0 recommended) | Auth0-PHP 8.0 | Composer
*/}
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/python/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/python/index.mdx
index 2c960a45f..2ded3b0e0 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/python/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/python/index.mdx
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ System requirements: Python 3 | Authlib 1.0 | Flask 2.0
*/}
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/rails/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/rails/index.mdx
index beeef8b79..7b2428e26 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/rails/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/rails/index.mdx
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ System requirements: Ruby 2.5.0+ | Rails 6.0+ or Rails 5.0+ or Rails 4.2+
*/}
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
@@ -217,7 +217,7 @@ end
-The final destination URL (the `returnTo` value) needs to be in the list of `Allowed Logout URLs` . See the [logout documentation](/docs/authenticate/login/logout/redirect-users-after-logout) for more.
+The final destination URL (the `returnTo` value) needs to be in the list of `Allowed Logout URLs` . See the [logout documentation](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/logout/redirect-users-after-logout) for more.
The user will now be able to logout of your application by visiting the `/auth/logout` endpoint.
- This loads the Auth0 login page into a web view. You can learn how to customize the login page at [this document](/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login#simple-customization).
+ This loads the Auth0 login page into a web view. You can learn how to customize the login page at [this document](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login#simple-customization).
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/windows-uwp-csharp/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/windows-uwp-csharp/index.mdx
index 5a726240d..902aa7941 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/windows-uwp-csharp/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/windows-uwp-csharp/index.mdx
@@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ System requirements: Microsoft Visual Studio 2017 | Windows 10 SDK (10.0.10586.0
*/}
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
@@ -102,7 +102,7 @@ var loginResult = await client.LoginAsync();

-This will load the Auth0 login page into a web view. You can learn how to customize the login page in [this document](/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login#simple-customization).
+This will load the Auth0 login page into a web view. You can learn how to customize the login page in [this document](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login#simple-customization).
## Handle Authentication Tokens
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/wpf-winforms/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/wpf-winforms/index.mdx
index b646aaaf1..eafb964a8 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/wpf-winforms/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/wpf-winforms/index.mdx
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ System requirements: Microsoft Visual Studio 2022 | .NET Framework 4.6.2 | .NET
*/}
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
@@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ If you are following along with the sample project you downloaded from the top o
### Install Dependencies
-The `Auth0.OidcClient.WPF` or `Auth0.OidcClient.WinForms` NuGet packages helps you authenticate users with any [Auth0 supported identity provider](/docs/authenticate/identity-providers).
+The `Auth0.OidcClient.WPF` or `Auth0.OidcClient.WinForms` NuGet packages helps you authenticate users with any [Auth0 supported identity provider](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/identity-providers).
Use the NuGet Package Manager (Tools -> Library Package Manager -> Package Manager Console) to install the `Auth0.OidcClient.WPF` or `Auth0.OidcClient.WinForms` package, depending on whether you are building a WPF or Windows Forms application:
@@ -98,7 +98,7 @@ var loginResult = await client.LoginAsync();

-This will load the Auth0 login page into a web view. You can learn how to customize the login page in [this document](/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login#simple-customization).
+This will load the Auth0 login page into a web view. You can learn how to customize the login page in [this document](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login#simple-customization).
## Handle Authentication Tokens
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/native/xamarin/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/native/xamarin/index.mdx
index 8e2ae56b7..66c3b726e 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/native/xamarin/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/native/xamarin/index.mdx
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ This quickstart focusses on .NET Android and iOS, as they are the next generatio
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Native Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/mobile-api) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow/authorization-code-flow-with-pkce) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/spa/flutter/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/spa/flutter/index.mdx
index e2baec73d..a7ad146c8 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/spa/flutter/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/spa/flutter/index.mdx
@@ -119,7 +119,7 @@ export const sections = [
- [Universal Login](/docs/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login) is
+ [Universal Login](https://auth0.com/docs/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login) is
the easiest way to set up authentication in your application. We recommend using it for the best experience, best
security, and the fullest array of features.
@@ -128,7 +128,7 @@ export const sections = [
You will normally need to specify the `redirectUrl` parameter to
- `loginWithRedirect`. Omitting this will cause Auth0 to use the [default login route](/docs/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login/configure-default-login-routes), which is not configured by default.
+ `loginWithRedirect`. Omitting this will cause Auth0 to use the [default login route](https://auth0.com/docs/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login/configure-default-login-routes), which is not configured by default.
When a user logs in, they are redirected back to your application. You are then able to access the ID and access
@@ -160,11 +160,11 @@ export const sections = [
To log users out, redirect them to the Auth0 logout endpoint to clear their login session by calling the Auth0
Flutter SDK `logout()`. [Read
- more about logging out of Auth0](/docs/docs/authenticate/login/logout).
+ more about logging out of Auth0](https://auth0.com/docs/docs/authenticate/login/logout).
You will normally want to specify `returnToUrl` when calling `logout`, otherwise
- Auth0 [will default to the first URL in the Allowed Logout URLs list](/docs/docs/authenticate/login/logout/redirect-users-after-logout).
+ Auth0 [will default to the first URL in the Allowed Logout URLs list](https://auth0.com/docs/docs/authenticate/login/logout/redirect-users-after-logout).
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-core-blazor-server/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-core-blazor-server/index.mdx
index fcd0f6177..cd62912b2 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-core-blazor-server/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-core-blazor-server/index.mdx
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ If you are following along with the sample project you downloaded from the top o
## Integrate Auth0
-[Universal Login](/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login) is the easiest way to set up authentication in your application. We recommend using it for the best experience, security, and the most complete array of features. This guide uses Universal Login to provide a way for your users to log in to your Blazor Server application.
+[Universal Login](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login) is the easiest way to set up authentication in your application. We recommend using it for the best experience, security, and the most complete array of features. This guide uses Universal Login to provide a way for your users to log in to your Blazor Server application.
### Install dependencies
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-core/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-core/index.mdx
index eddcbc9f9..d5f6ca20f 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-core/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-core/index.mdx
@@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ If you are following along with the sample project you downloaded from the top o
## Integrate Auth0
-[Universal Login](/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login) is the easiest way to set up authentication in your application. We recommend using it for the best experience, best security and the fullest array of features. This guide will use it to provide a way for your users to log in to your ASP.NET Core application.
+[Universal Login](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login) is the easiest way to set up authentication in your application. We recommend using it for the best experience, best security and the fullest array of features. This guide will use it to provide a way for your users to log in to your ASP.NET Core application.
### Install dependencies
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-owin/_index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-owin/_index.mdx
index 715e4167a..16c432ea6 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-owin/_index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-owin/_index.mdx
@@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ export const sections = [
For the SDK to function properly, set the following properties in `Web.config`:
- - `auth0:Domain`: The domain of your Auth0 tenant. You can find this in the Auth0 Dashboard under your application's **Settings **in the Domain field. If you are using a [custom domain](/docs/customize/custom-domains), set this to the value of your custom domain instead.
+ - `auth0:Domain`: The domain of your Auth0 tenant. You can find this in the Auth0 Dashboard under your application's **Settings **in the Domain field. If you are using a [custom domain](https://auth0.com/docs/customize/custom-domains), set this to the value of your custom domain instead.
- `auth0:ClientId`: The ID of the Auth0 application you created in Auth0 Dashboard. You can find this in the Auth0 Dashboard under your application's **Settings **in the Client ID field.
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-owin/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-owin/index.mdx
index ea654a3ea..f33aafdbe 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-owin/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/aspnet-owin/index.mdx
@@ -169,7 +169,7 @@ public void Configuration(IAppBuilder app)
It is essential that you register both the cookie middleware and the OpenID Connect middleware, as they are required (in that order) for the authentication to work. The OpenID Connect middleware will handle the authentication with Auth0. Once the user has authenticated, their identity will be stored in the cookie middleware.
-In the code snippet above, note that the `AuthenticationType` is set to **Auth0**. This will be used in the next section to challenge the OpenID Connect middleware and start the authentication flow. Also note code in the `RedirectToIdentityProvider` notification event which constructs the correct [logout URL](/docs/authenticate/login/logout).
+In the code snippet above, note that the `AuthenticationType` is set to **Auth0**. This will be used in the next section to challenge the OpenID Connect middleware and start the authentication flow. Also note code in the `RedirectToIdentityProvider` notification event which constructs the correct [logout URL](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/logout).
## Add login to your ASP.NET OWIN application
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/django/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/django/index.mdx
index ad45b77fc..67a7ffc53 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/django/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/django/index.mdx
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ System requirements: Python 3 | Authlib 1.0 | Django 4.0
*/}
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/golang/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/golang/index.mdx
index 24296c24c..c8c95b589 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/golang/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/golang/index.mdx
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ System requirements: Go 1.21+
*/}
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
@@ -478,12 +478,12 @@ func Handler(ctx *gin.Context) {
-For information about the userinfo hash, see [User Profile](/docs/manage-users/user-accounts/user-profiles).
+For information about the userinfo hash, see [User Profile](https://auth0.com/docs/manage-users/user-accounts/user-profiles).
## Logging Out
To log the user out, clear the data from the session and redirect the user to the Auth0 logout endpoint. You can find
-more information about this in the [logout documentation](/docs/authenticate/login/logout).
+more information about this in the [logout documentation](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/logout).
Create a file called `logout.go` in the folder `web/app/logout/logout.go`, and add the function `Handler` to redirect
the user to Auth0's logout endpoint.
@@ -534,7 +534,7 @@ func Handler(ctx *gin.Context) {
-The redirect URL needs to be in the list of Allowed Logout URLs in the settings section of the application, For more information, see [Redirect Users After Logout](/docs/authenticate/login/logout/guides/redirect-users-after-logout).
+The redirect URL needs to be in the list of Allowed Logout URLs in the settings section of the application, For more information, see [Redirect Users After Logout](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/logout/guides/redirect-users-after-logout).
Create a file called `user.js` in the folder `web/static/js`, and add the code to remove the cookie from a logged-in
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java-ee/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java-ee/index.mdx
index 4e07d03af..ef9e7a3f3 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java-ee/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java-ee/index.mdx
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ System requirements: Java 11
*/}
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java-spring-boot/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java-spring-boot/index.mdx
index ddebdd3f6..1ac206893 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java-spring-boot/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java-spring-boot/index.mdx
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ This tutorial uses [Spring MVC](https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/sprin
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java/index.mdx
index 30d06fb17..d4bdef338 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/java/index.mdx
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ System requirements: Java 8 | Gradle 3.3 and up
*/}
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
@@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ If you are following along with the sample project you downloaded from the top o
To integrate your Java application with Auth0, add the following dependencies:
* **javax.servlet-api**: is the library that allows you to create Java Servlets. You then need to add a Server dependency like Tomcat or Gretty, which one is up to you. Check our sample code for more information.
-* **auth0-java-mvc-commons**: is the [Java library](https://github.com/auth0/auth0-java-mvc-common) that allows you to use Auth0 with Java for server-side MVC web apps. It generates the Authorize URL that you need to call in order to authenticate and validates the result received on the way back to finally obtain the [Auth0 Tokens](/docs/secure/tokens) that identify the user.
+* **auth0-java-mvc-commons**: is the [Java library](https://github.com/auth0/auth0-java-mvc-common) that allows you to use Auth0 with Java for server-side MVC web apps. It generates the Authorize URL that you need to call in order to authenticate and validates the result received on the way back to finally obtain the [Auth0 Tokens](https://auth0.com/docs/secure/tokens) that identify the user.
If you are using Gradle, add them to your `build.gradle`:
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/php/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/php/index.mdx
index 3b4e551c1..c3b4cbb84 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/php/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/php/index.mdx
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ System requirements: PHP 7.4+ (8.0 recommended) | Auth0-PHP 8.0 | Composer
*/}
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/python/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/python/index.mdx
index 2c960a45f..2ded3b0e0 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/python/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/python/index.mdx
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ System requirements: Python 3 | Authlib 1.0 | Flask 2.0
*/}
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
diff --git a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/rails/index.mdx b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/rails/index.mdx
index beeef8b79..7b2428e26 100644
--- a/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/rails/index.mdx
+++ b/main/docs/quickstart/webapp/rails/index.mdx
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ System requirements: Ruby 2.5.0+ | Rails 6.0+ or Rails 5.0+ or Rails 4.2+
*/}
-**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
+**New to Auth?** Learn [How Auth0 works](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/auth0-overview), how it [integrates with Regular Web Applications](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/architecture-scenarios/sso-for-regular-web-apps) and which [protocol](https://auth0.com/docs/get-started/authentication-and-authorization-flow) it uses.
## Configure Auth0
@@ -217,7 +217,7 @@ end
-The final destination URL (the `returnTo` value) needs to be in the list of `Allowed Logout URLs` . See the [logout documentation](/docs/authenticate/login/logout/redirect-users-after-logout) for more.
+The final destination URL (the `returnTo` value) needs to be in the list of `Allowed Logout URLs` . See the [logout documentation](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/logout/redirect-users-after-logout) for more.
The user will now be able to logout of your application by visiting the `/auth/logout` endpoint.
 - This loads the Auth0 login page into a web view. You can learn how to customize the login page at [this document](/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login#simple-customization).
+ This loads the Auth0 login page into a web view. You can learn how to customize the login page at [this document](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login#simple-customization).
- This loads the Auth0 login page into a web view. You can learn how to customize the login page at [this document](/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login#simple-customization).
+ This loads the Auth0 login page into a web view. You can learn how to customize the login page at [this document](https://auth0.com/docs/authenticate/login/auth0-universal-login#simple-customization).