参考 Skip Lists: A Probabilistic Alternative to Balanced Trees
个人理解,有错误,欢迎指正。
To get away from magic constants, we say that a fraction p of the nodes with level i pointers also have level i+1 point- ers. (for our original discussion, p = 1/2).
假定 P 代表第i层元素有第i+1层的概率,且 p 是一个常数。(这里假定p=1/2)
Our analysis suggests that ideally we would start a search at the level L where we expect 1/p nodes.
理想情况下,搜索从L层搜索,它期望的节点是1/p个。
现在要推导出L( or i)、p、n 之间的关系。
- 某个元素拥有第
i层的概率是 `p^(i-1)。 - 第
i层拥有的元素个数的数学期望为n*p^(i-1)。 - 则有
1/p= n*p^(i-1)
1/p=n*p^(i-1)
n=p^(-i)
// 替换 i 为 l
n=(1/p)^(l)
// 同时求对数
lnn=l*ln(1/p)
l = log_1/p(n)
解之可得: l = log_1/p(n) = L(n)
因此当 p=1/2 时,max_level=16 时,n=2^16
查询、删除和增加时间复杂度分析
由于已知节点的删除和增加元素是常数时间,因此其复杂度归根于查询的时间复杂度。
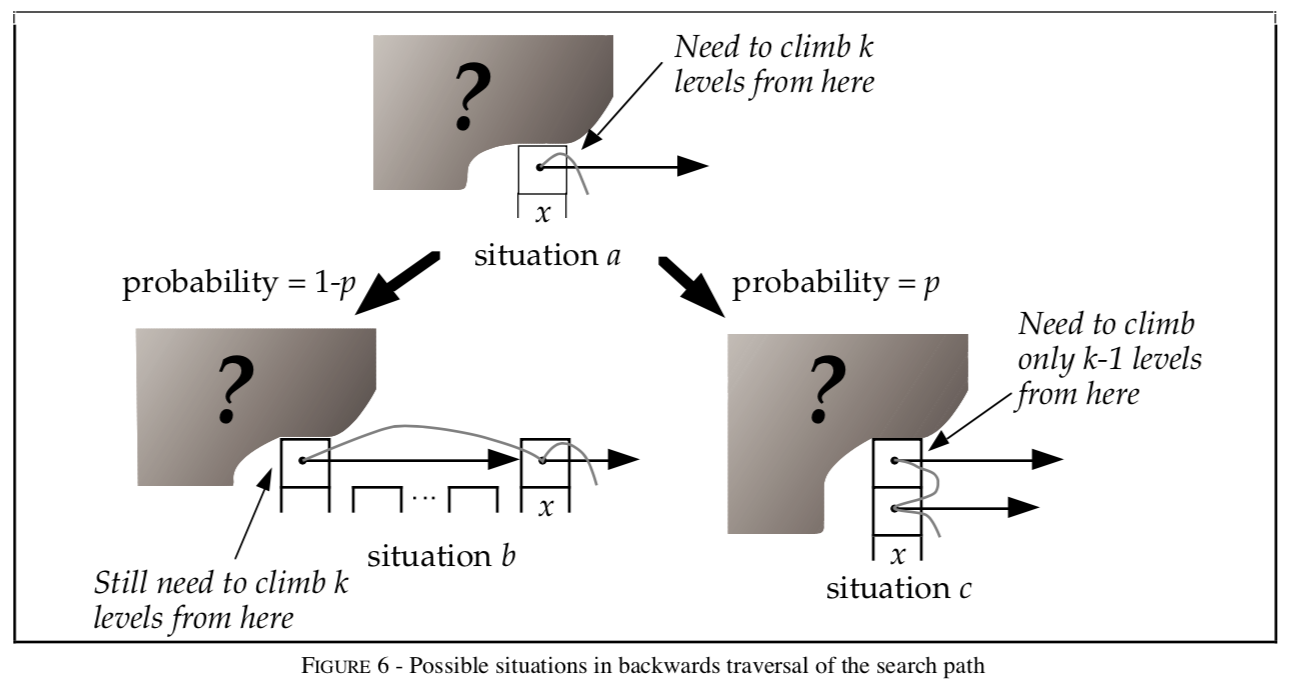
We analyze the search path backwards, travelling up and to the left. Although the levels of nodes in the list are known and fixed when the search is performed, we act as if the level of a node is being determined only when it is observed while backtracking the search path.
At any particular point in the climb, we are at a situation similar to situation a in Figure 6 – we are at the ith forward pointer of a node x and we have no knowledge about the levels of nodes to the left of x or about the level of x, other than that the level of x must be at least i. Assume the x is not the header (the is equivalent to assuming the list extends in- finitely to the left). If the level of x is equal to i, then we are in situation b. If the level of x is greater than i, then we are in situation c. The probability that we are in situation c is p. Each time we are in situation c, we climb up a level. Let C(k) = the expected cost (i.e, length) of a search path that climbs up k levels in an infinite list:
(看的头晕~~~~)
这里假设是类似于回溯的方式,向左和向上爬升。
在某个爬升的特定节点x,它处于它的第i层上(显而易见,节点x的层级至少是i)。当它的层级刚好是i时,它处于situation b 情况,此时它向左爬行。当它的层级大于i时,它处于situation c情况,此时它向上爬行一格(注意,此情况的概率刚好为p,数学真是巧妙~~~)。
我们用c(k)代表节点向上爬行的格数大小(k)的期望。
因此有:
c(0) = 0
c(k) = (1-p)(1+c(k))+p*(1+c(k-1))
化简合并为(数列求值): c(k) = k/p (吊炸天。。。)
这里展开详细解释一下:
c(k) = (1-p)(1+c(k))+p*(1+c(k-1))
右侧根据+后分为两项,刚好对应情况b和c。
情况b:
其概率为(1-p),对应的路径长度为 1(向左移一位)+c(k)(下一个节点对应的k的期望,刚好也是c(k))
情况c:
概率是p(看p的定义),路径长度+1(向上移位),+ 上一个节点的对于的k-1的期望,为c(k-1)
给一个最坏的情况,一直向上爬,那么爬到上线(max_level)的期望为:
T = (L(n)-1)/p = (log_(1/p)n-1)/p
p=1/2 时,T = logn-1/2
即平均查找长度为 (log_(1/p)n-1)/p = O(logN)
// todo
后面看不太懂了~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~