We've created a special docker-compose.dev.yml override file that should configure docker images to be easier to use
during development.
Normally, you'd rebuild your images from scratch with a combination of gradle and docker compose commands. However, this takes way too long for development and requires reasoning about several layers of docker compose configuration yaml files which can depend on your hardware (Apple M1).
The docker-compose.dev.yml file bypasses the need to rebuild docker images by mounting binaries, startup scripts,
and other data. These dev images, tagged with debug will use your locally built code with gradle.
Building locally and bypassing the need to rebuild the Docker images should be much faster.
We highly recommend you just invoke ./gradlew quickstartDebug task.
./gradlew quickstartDebugThis task is defined in docker/build.gradle and executes the following steps:
-
Builds all required artifacts to run DataHub. This includes both application code such as the GMS war, the frontend distribution zip which contains javascript, as well as secondary support docker containers.
-
Locally builds Docker images with the expected
debugtag required by the docker compose files. -
Runs the special
docker-compose.dev.ymland supporting docker-compose files to mount local files directly in the containers with remote debugging ports enabled.
Once the debug docker images are constructed you'll see images similar to the following:
acryldata/datahub-frontend-react debug e52fef698025 28 minutes ago 763MB
acryldata/datahub-kafka-setup debug 3375aaa2b12d 55 minutes ago 659MB
acryldata/datahub-gms debug ea2b0a8ea115 56 minutes ago 408MB
acryldata/datahub-upgrade debug 322377a7a21d 56 minutes ago 463MB
acryldata/datahub-mysql-setup debug 17768edcc3e5 2 hours ago 58.2MB
acryldata/datahub-elasticsearch-setup debug 4d935be7c62c 2 hours ago 26.1MBAt this point it is possible to view the DataHub UI at http://localhost:9002 as you normally would with quickstart.
Like quickStartDebug, there are a few other tasks that bring up a different set of containers, for example
quickStartDebugConsumers will also bring up mce-consumer and mae-consumer.
Next, perform the desired modifications
To see these changes in the deployment, a rebuilt of modified artifacts and a restart of the container(s) is required to run with the updated code. The restart can be performed using following gradle task.
./gradlew :docker:debugReloadThis single task will build the artifacts that were modified and restart only those containers that were affected by the rebuilt artifacts.
For each of the quickStartDebug variants, there is a corresponding debugReload task.
For quickStartDebugConsumers, the reload task is debugConsumersReload
debugReload is generally much faster than re-running quickStartDebug and is recommended after an initial bringup of all services via quickStartDebug followed
by loading the incremental changes using debugReload.
If there are significant changes to the code, for example due to pulling the latest code, it is recommended to start with a quickStartDebug and then iterate using debugReload
You can define different sets of environment variables for all the containers in an env file. The env files must be located in the docker/profiles folder.
To use the env file, run
DATAHUB_LOCAL_COMMON_ENV=my-settings.env ./gradlew quickStartDebugThe debugReload process continues to work, but the restarted containers will use the same settings that were present at the time of running ./gradlew quickStartDebug.
If you need to reload the containers with a different env file or changes made to the env file, a task debugReloadEnv builds the artifacts that have code changes
and recreates all the containers that refer to these the env file via the DATAHUB_LOCAL_COMMON_ENV environment variable.
debugReloadEnv also has variants for all the quickStartDebug variants. For example, quickStartDebugConsumers has debugConsumersReloadEnv
The following commands can pause the debugging environment to release resources when not needed.
Pause containers and free resources.
docker compose -p datahub stopResume containers for further debugging.
docker compose -p datahub startThe default debugging process uses your local code and enables debugging by default for both GMS and the frontend. Attach to the instance using your IDE by using its Remote Java Debugging features.
Environment variables control the debugging ports for GMS and the frontend.
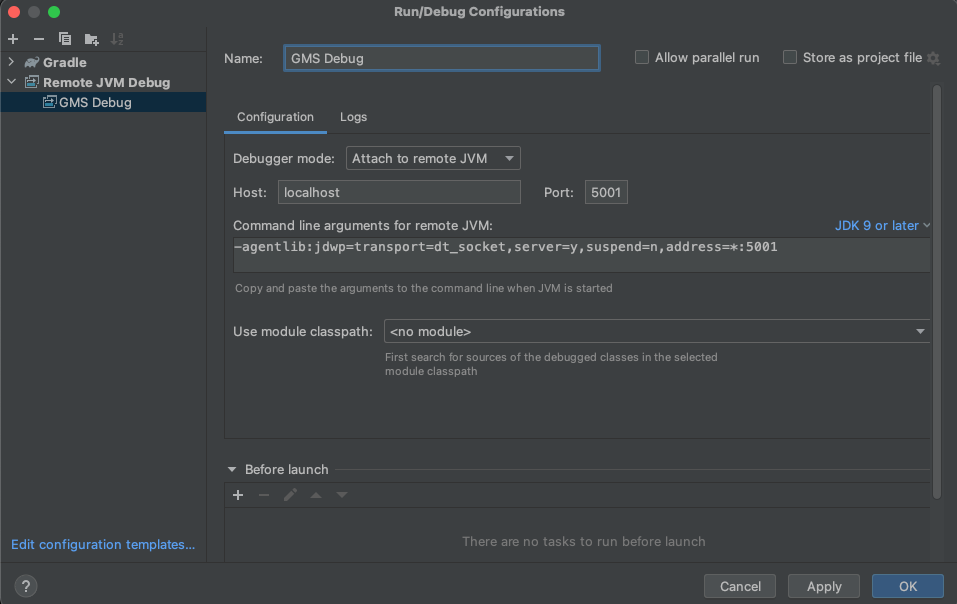
DATAHUB_MAPPED_GMS_DEBUG_PORT- Default: 5001DATAHUB_MAPPED_FRONTEND_DEBUG_PORT- Default: 5002
The screenshot shows an example configuration for IntelliJ using the default GMS debugging port of 5001.
It is highly recommended you use Docker Desktop's dashboard to access service logs. If you double click an image it will pull up the logs for you.
If you run quickstart, use ./gradlew quickstartDebug to return to using the debugging containers.
If you run into disk space issues and prune the images & containers you will need to execute the ./gradlew quickstartDebug
again.
The datahub-upgrade job will not block the startup of the other containers as it normally
does in a quickstart or production environment. Normally this is process is required when making updates which
require Elasticsearch reindexing. If reindexing is required, the UI will render but may temporarily return errors
until this job finishes.
docker-compose up will launch all services in the configuration, including dependencies, unless they're already
running. If you, for some reason, wish to change this behavior, check out these example commands.
docker-compose -p datahub -f docker-compose.yml -f docker-compose.override.yml -f docker-compose-without-neo4j.m1.yml -f docker-compose.dev.yml up datahub-gms
Will only start datahub-gms and its dependencies.
docker-compose -p datahub -f docker-compose.yml -f docker-compose.override.yml -f docker-compose-without-neo4j.m1.yml -f docker-compose.dev.yml up --no-deps datahub-gms
Will only start datahub-gms, without dependencies.