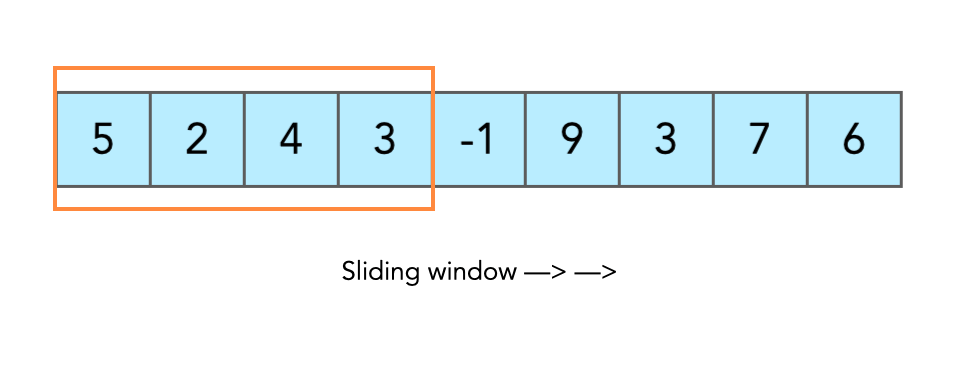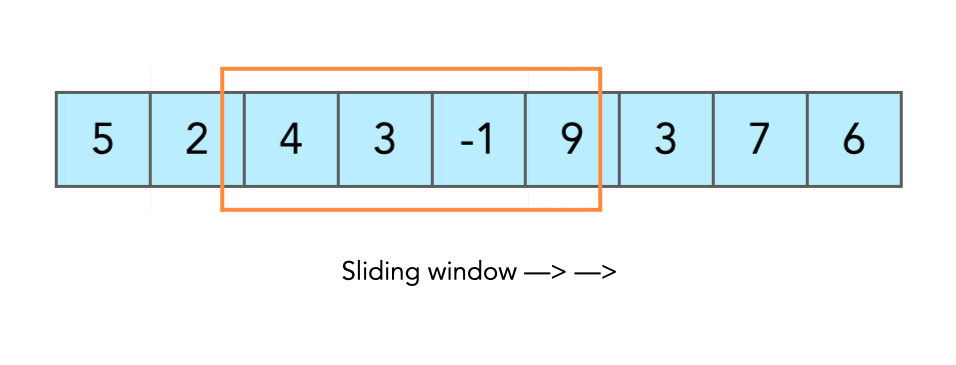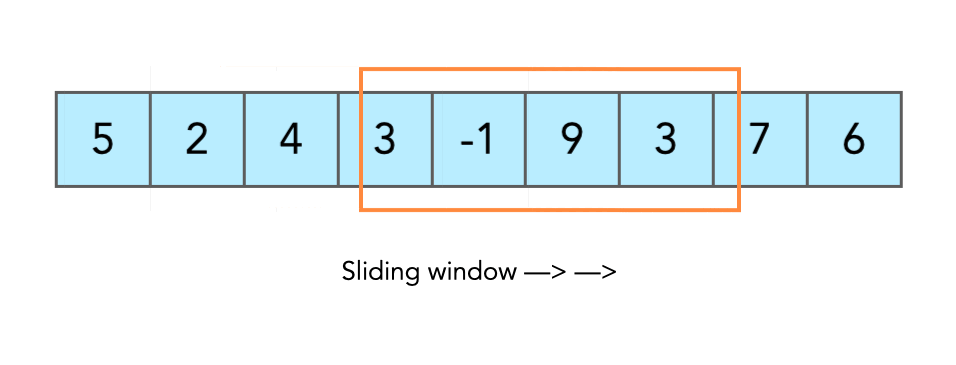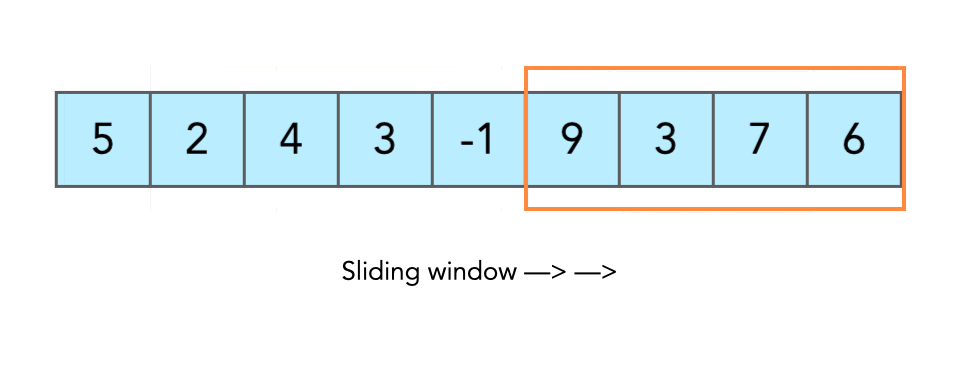
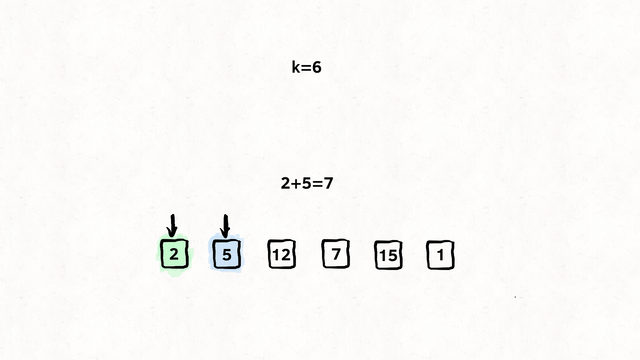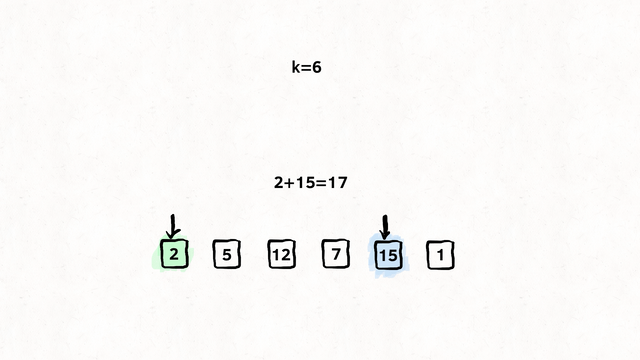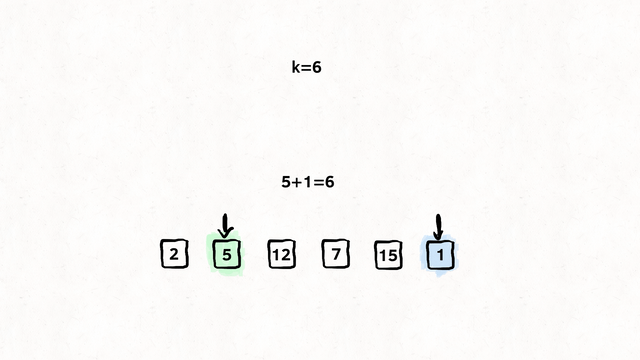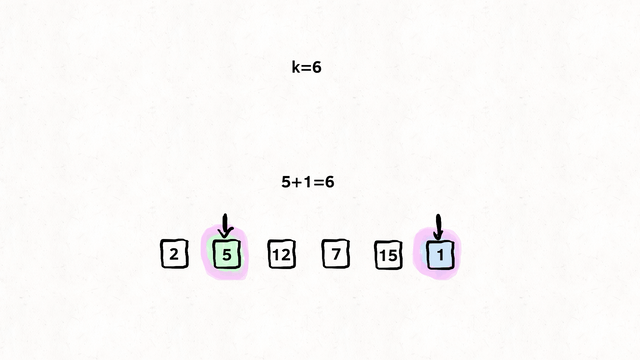-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
Home

Planned Courses
- Algorithm 2
- Algorithm 3
- Graph Theory 1
- Graph Theory 2
- Graph Theory 3
- Binary Search 1
- Binary Search 2
- Binary Search 3
- Dynamic Programming 1
- Dynamic Programming 2
- Dynamic Programming 3
- Dynamic Programming 4
Given an array nums of distinct integers, return all the possible permutations. You can return the answer in any order.
Input: nums = [1,2,3]
Output: 1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1
var permute = function(nums) {
let res = [];
let cur = new Set();
function backtrack() {
if (cur.size === nums.length) {
res.push([...cur]);
return;
}
for (let n of nums) {
if (cur.has(n)) {
continue;
}
cur.add(n);
backtrack();
cur.delete(n);
}
}
backtrack();
return res;
};Given a string s, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
Input: s = "abcabcbb"
Output: 3
Explanation: The answer is "abc", with the length of 3.
var lengthOfLongestSubstring = function(s) {
let set = new Set();
let max = 0;
let left = 0;
for (let right = 0; right < s.length; right++) {
while (set.has(s[right])) {
set.delete(s[left++]);
}
set.add(s[right]);
max = Math.max(max, right - left + 1);
}
return max;
};Question:
Decode this string.
Input: s = "3[a]2[bc]"
Output: "aaabcbc"
const decodeString = s => {
const stack = [];
for (const char of s) {
if (char !== "]") { stack.push(char); continue; }
let cur = stack.pop();
let str = '';
while (cur !== '[') {
str = cur + str;
cur = stack.pop();
}
let num = '';
cur = stack.pop();
while (!Number.isNaN(Number(cur))) {
num = cur + num;
cur = stack.pop();
}
stack.push(cur);
stack.push(str.repeat(Number(num)));
}
return stack.join('');
};Question:
Determine valid parentheses.
Input: s = "()[]{}"
Output: true
var isValid = function(s) {
const stack = [];
const map = {
'(': ')',
'[': ']',
'{': '}'
}
for (let i = 0 ; i < s.length ; i++) {
let c = s[i];
if (map[c]) {
stack.push(map[c])
} else if (c !== stack.pop()) {
return false;
}
}
return !stack.length;
};Return the maximum amount of water a container can store.

Input: height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
Output: 49
Explanation: The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
var maxArea = function(height) {
let left = 0;
let right = height.length - 1;
let max = 0;
while (left <= right) {
let curArea = Math.min(height[left], height[right]) * (right - left);
if (height[left] <= height[right]) {
left++;
} else {
right--;
}
max = Math.max(max, curArea);
}
return max;
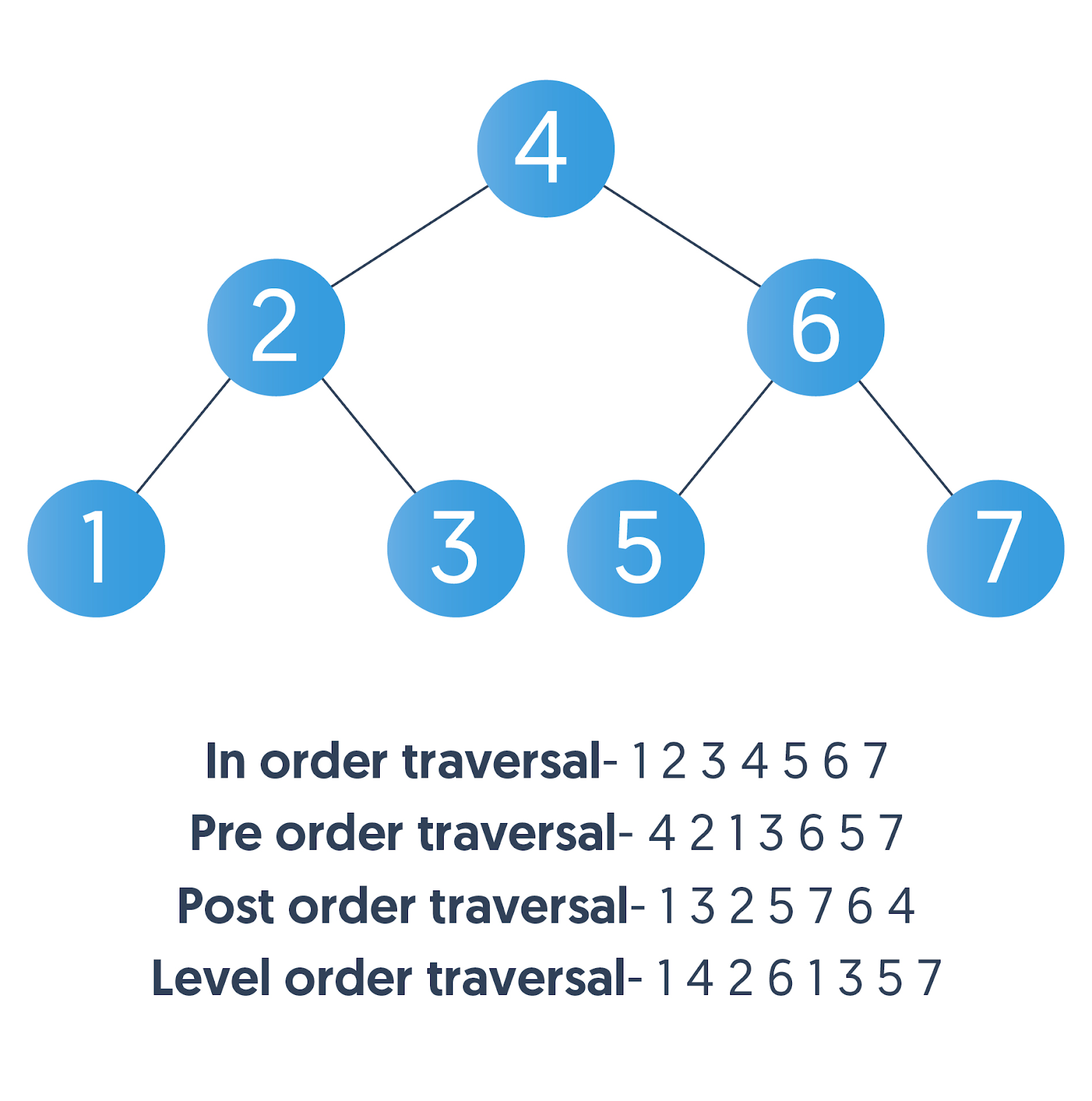
};Given the root of a binary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes' values. (i.e., from left to right, level by level).

Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 3],[9,20],[15,7
var levelOrder = function(root) {
if(!root) return [];
let q = [root];
let res = [];
while (q.length !== 0) {
let temp = [];
let len = q.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
let c = q.shift();
temp.push(c.val);
c.left && q.push(c.left);
c.right && q.push(c.right);
}
res.push(temp);
}
return res;
};Left-> Root -> Right
Root-> Left -> Right
Left-> Right -> Root
Question:
Find the total sum of all root-to-leaf numbers. A leaf node is a node with no children.

Input: root = [1,2,3]
Output: 25
Explanation:
The root-to-leaf path 1->2 represents the number 12.
The root-to-leaf path 1->3 represents the number 13.
Therefore, sum = 12 + 13 = 25.
var sumNumbers = function(root) {
let res = [];
function dfs(node, path) {
if (!node) {
return false;
}
path.push(node.val);
if (!node.left && !node.right) {
res.push(Number(path.join("")));
return true;
}
node.left && dfs(node.left, [...path]);
node.right && dfs(node.right, [...path]);
}
dfs(root, []);
let answer = res.reduce((a, b) => a + b);
return answer;
};Question:
Find the number of islands in a grid.

Output: 3
var numIslands = function(grid) {
let rows = grid.length;
let cols = grid[0].length;
let res = 0;
function dfs(r, c) {
if (r < 0 || c < 0 || r >= rows || c >= cols || !grid[r][c] || grid[r][c] === '0') {
return;
}
grid[r][c] = '0';
dfs(r - 1, c);
dfs(r + 1, c);
dfs(r, c - 1);
dfs(r, c + 1);
}
for (let r = 0; r < rows; r++) {
for (let c = 0; c < cols; c++) {
if (grid[r][c] === '1') {
res++;
dfs(r, c);
}
}
}
return res;
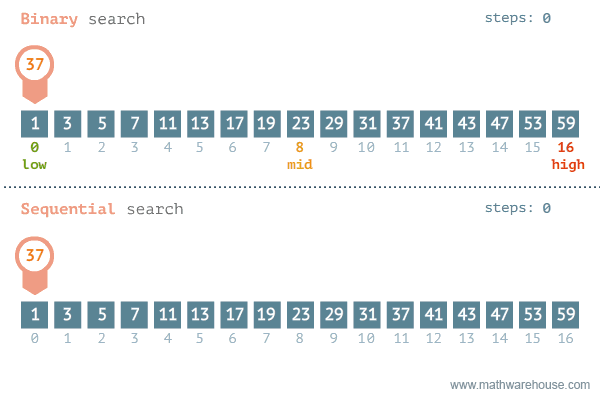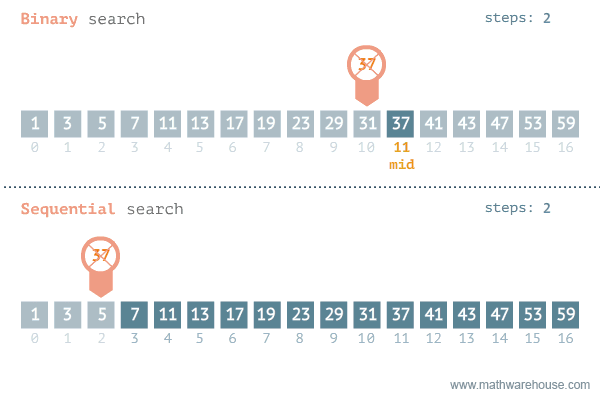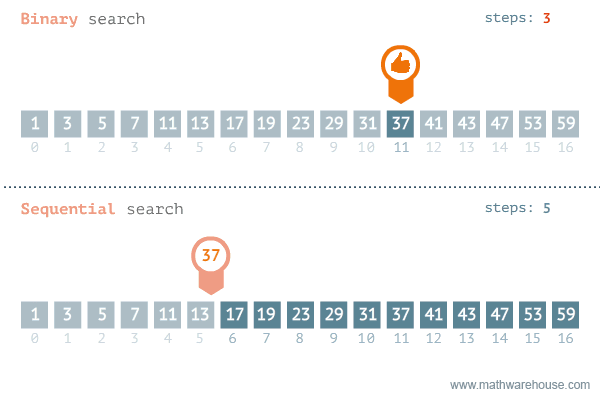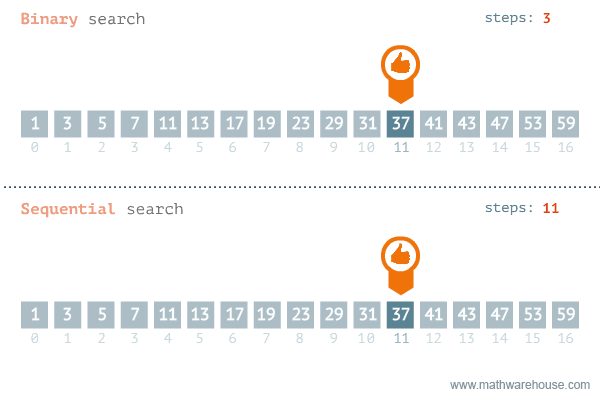
};Find if target exists in array. You must write an algorithm with O(log n) time complexity.
Input: nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 9
Output: 4
Explanation: 9 exists in nums and its index is 4
var search = function(nums, target) {
let left = 0;
let right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
let mid = Math.floor((right + left) / 2);
if (nums[mid] === target) {
return mid;
}
if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return -1;
};
Find the shortest path from k to n

Input: times = 2,1,1],[2,3,1],[3,4,1, n = 4, k = 2
Output: 2
var networkDelayTime = function (times, n, k) {
// Our return value, how long did it take
// to reach all nodes within the network from {k}
let time_taken = 0;
// A set so we don't visit the same node twice.
const visited_set = new Set();
const min_heap = new MinPriorityQueue();
// An adjacency list, where we store
// Node -> [[Edge, Cost],[Edge, Cost]]
const node_edge_cost = new Map();
// Build the adjacency list.
for (const [node, edge, cost] of times) {
let edges = [];
if (node_edge_cost.has(node)) {
edges = node_edge_cost.get(node);
}
edges.push([edge, cost]);
node_edge_cost.set(node, edges);
}
// We have been asked to start at {k}
// So we enqueue {k} at the cost of 0, as of course
// it costs nothing as we start here.
min_heap.enqueue([k, 0], 0);
while (min_heap.size()) {
// Get the cheapest operation relative to {k}
// Node and cost
const [node, cost] = min_heap.dequeue().element;
// Have we already been here? No loops today kiddo
if (visited_set.has(node)) continue;
// Set it. We don't want to come back here.
visited_set.add(node);
// Did our distance increase?
// If so, update it. If not, keep the same
time_taken = Math.max(cost, time_taken);
// Get the edges for this node (If any)
const node_edges = node_edge_cost.get(node) || [];
for (const [edge_node, edge_cost] of node_edges) {
if (!visited_set.has(edge_node)) {
// Add it to the queue, set the priority to the cost of the edge
// So we only ever visit the cheapest edge.
min_heap.enqueue([edge_node, edge_cost + cost], edge_cost + cost);
}
}
}
// Did we visit every node?
// If not, we failed to spread the message across the network.
// If so, return the time taken.
return visited_set.size === n ? time_taken : -1;
};Time Complexity: O(E log V)
Works when there is negative weight edge. Slower than Dijkstra.
var networkDelayTime = function(times, n, k) {
let arr = new Array(n + 1).fill(Infinity);
arr[k] = 0;
for (let i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
let temp = arr.slice();
for (let [source, target, cost] of times) {
if (temp[source] === Infinity) continue;
temp[target] = Math.min(temp[target], temp[source] + cost);
}
arr = temp;
}
arr.shift();
let res = Math.max(...arr);
return res === Infinity ? -1 : res;
};Time Complexity: O ( V ⋅ E )
Find all possible paths from source to target. Return them in any order.

Input: graph = 1,2],[3],[3],[
Output: 0,1,3],[0,2,3
Explanation: There are two paths: 0 -> 1 -> 3 and 0 -> 2 -> 3.
var allPathsSourceTarget = function(graph) {
let res = [];
let target = graph.length - 1;
function dfs(node, path) {
path.push(node);
if (node === target) {
res.push(path);
return;
}
let visiting = graph[node];
for(let cur of visiting) {
dfs(cur, [...path])
}
}
dfs(0, []);
return res;
};Return the minimum cost to make all points connected. All points are connected if there is exactly one simple path between any two points.

Input: points = 0,0],[2,2],[3,10],[5,2],[7,0
Output: 20
**Explanation: **

We can connect the points as shown above to get the minimum cost of 20. Notice that there is a unique path between every pair of points.
var minCostConnectPoints = function(points) {
let cost = 0;
let n = points.length;
let dist = new Array(n).fill(Infinity);
dist[0] = 0;
let next = 0;
for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
let min = Infinity;
let point = -1;
for (let j = 1; j < n; j++) {
let [x1, y1] = points[j];
let [x2, y2] = points[next];
if (dist[j] > 0) {
dist[j] = Math.min(dist[j], Math.abs(x1 - x2) + Math.abs(y1 - y2));
if (dist[j] < min) {
min = dist[j];
point = j;
}
}
}
cost += min;
dist[point] = 0;
next = point;
}
return cost;
};Return the correct order you should take to finish all courses.
Input: numCourses = 4, prerequisites = 1,0],[2,0],[3,1],[3,2
Output: [0,2,1,3]
Explanation: There are a total of 4 courses to take. To take course 3 you should have finished both courses 1 and 2. Both courses 1 and 2 should be taken after you finished course 0. So one correct course order is [0,1,2,3]. Another correct ordering is [0,2,1,3].
var findOrder = function(numCourses, prerequisites) {
let preMap = new Map();
//Create a set, not an array, so that we do not add visited nodes
let res = new Set();
let visited = new Set();
//create adjList
for (let [crs, pre] of prerequisites) {
preMap.set(crs, (preMap.get(crs) || []).concat(pre));
}
function dfs(node) {
if (visited.has(node)) return false;
visited.add(node);
let visiting = preMap.get(node);
while (visiting && visiting.length > 0) {
let c = visiting.shift();
if (!dfs(c)) return false;
}
visited.delete(node);
res.add(node);
return true;
}
for (let i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (!dfs(i)) return [];
}
return [...res];
};Time Complexity: O(V+E), where V = vertices, E = Edges.
A Union-Find data structure is to maintain a set of elements partitioned into a number of mutually disjoint (non-overlapping) subsets. So no elements belong to more than one set.
Applications:
-
connected component in Graph problem.
-
detecting cycles in graph.
-
minimum spanning tree.
Question:
Find the number of connected components in the graph.
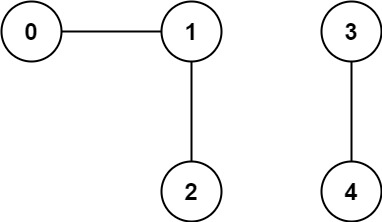
Input: n = 5, edges = 0,1],[1,2],[3,4
Output: 2
var countComponents = function(n, edges) {
let arr = [];
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr.push(i);
}
function find(n) {
let p = arr[n];
while (p !== arr[p]) {
p = arr[p];
}
return p;
}
for (let [src, dst] of edges) {
let p1 = find(src);
let p2 = find(dst);
if (p1 !== p2) {
arr[p1] = arr[p2];
n--;
}
}
return n;
};Time Complexity: O(log n)
Given an array of intervals where intervals[i] = [starti, endi], merge all overlapping intervals, and return an array of the non-overlapping intervals that cover all the intervals in the input.
Input: intervals = 1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18
Output: 1,6],[8,10],[15,18
Explanation: Since intervals [1,3] and [2,6] overlap, merge them into [1,6].

var merge = function(intervals) {
intervals.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
let prev = intervals[0];
let res = [prev];
for (let i = 0; i < intervals.length; i++) {
let c = intervals[i];
if (c[0] <= prev[1]) {
prev[1] = Math.max(prev[1], c[1]);
} else {
res.push(c);
prev = c;
}
}
return res;
}; Return true if there is a cycle in the linked list. Otherwise, return false.

Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 1st node (0-indexed).
var hasCycle = function(head) {
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
while (fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow === fast) return true;
}
return false;
};Heaps are structures meant to allow quick access to the min or the max.
Can get acccess to max or min at constant time O(1)
Time complexity: O(nlogn)
MaxPriorityQueue
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return the k most frequent elements. You may return the answer in any order.
Input: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2
Output: [1,2]
var topKFrequent = function(nums, k) {
let map = new Map();
let maxHeap = new MaxPriorityQueue(item => item.value);
// O(n) Time complexity
for (let num of nums) {
map.set(num, (map.get(num) || 0) + 1);
}
let ans = [];
// We are building a maxHeap for the D unique item
// O(D) time complexity
for (let [key, value] of map) {
maxHeap.enqueue(key, value);
}
for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {
// We are dequeuing the k elements which can take upto O(klogD)
let _item = maxHeap.dequeue();
ans.push(_item.element);
}
return ans;
};MinPriorityQueue
Return the closest point to origin.

Input: points = 1,3],[-2,2, k = 1
Output: -2,2
var kClosest = function(points, k) {
let q = new MinPriorityQueue({ priority: (x) => x[0] });
let res = [];
function calculateDis([a, b]) {
return a * a + b * b;
}
for (let p of points) {
q.enqueue([calculateDis(p), p]);
}
for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {
let c = q.dequeue().element;
res.push(c[1]);
}
return res;
};Greedy is an algo approach that builds up a solution piece by piece, always choosing the next piece that offers that most obvious and immediate benefit. So the problems where choosing locally optimal also leads to global solution are the best fit for Greedy.
Question:
Given an integer array nums, find the subarray which has the largest sum and return its sum.
Input: nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]
Output: 6
Explanation: [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum = 6.
var maxSubArray = function(nums) {
let res = nums[0];
let curMax = 0;
for (let n of nums) {
if (curMax < 0) {
curMax = 0;
}
curMax += n;
res = Math.max(res, curMax);
}
return res;
};Given an integer array nums, return the length of the longest strictly increasing subsequence.
Input: nums = [10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18]
Output: 4
Explanation: The longest increasing subsequence is [2,3,7,101], therefore the length is 4.
var lengthOfLIS = function(nums) {
const dp = new Array(nums.length).fill(1);
for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[j]) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
}
}
}
return Math.max(...dp);
};You are climbing a staircase. It takes n steps to reach the top.
Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
Input: n = 3
Output: 3
Explanation: There are three ways to climb to the top.
-
1 step + 1 step + 1 step
-
1 step + 2 steps
-
2 steps + 1 step
var climbStairs = function(n) {
let memo = [];
function dfs(step, end) {
if (step === end) {
return 1;
}
if (end < step) {
return 0;
}
if (memo[step]) {
return memo[step];
}
memo[step] = dfs(step + 1, end) + dfs(step + 2, end);
return memo[step];
}
return dfs(0, n);
};Given an m x n board of characters and a list of strings words, return all words on the board.

Input: board = "o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v", words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"]
Output: ["eat","oath"]
var findWords = function(board, words) {
let rows = board.length;
let cols = board[0].length;
let res = new Set();
let visited = new Array(rows).fill(false).map(() => new Array(cols).fill(false));
function TrieNode() {
this.children = new Map();
this.end = false;
}
let root = new TrieNode();
function add(word) {
let cur = root;
for (let c of word) {
if (!cur.children.has(c)) {
cur.children.set(c, new TrieNode());
}
cur = cur.children.get(c);
}
cur.end = true;
}
//add all the words to Trie
for (let word of words) {
add(word);
}
function dfs(r, c, node, word) {
if (r < 0 || r >= rows || c < 0 || c >= cols || visited[r][c] || !node.children.get(board[r][c])) {
return;
}
visited[r][c] = true;
word += board[r][c];
node = node.children.get(board[r][c]);
if (node.end) {
res.add(word);
}
dfs(r - 1, c, node, word);
dfs(r + 1, c, node, word);
dfs(r, c - 1, node, word);
dfs(r, c + 1, node, word);
visited[r][c] = false;
}
for (let r = 0; r < rows; r++) {
for (let c = 0; c < cols; c++) {
dfs(r, c, root, '');
}
}
return [...res];
};Creates a new Set
new Set()
const myArray = ["a","b","c"];
const letters = new Set(myArray);Adds a new element to the Set
letters.add("a");Removes an element from a Set
letters.delete("a");Returns true if a value exists in the Set
let res = letters.has("a");
res = trueReturns the number of elements in a Set
const myArray = ["a","b","c"];
const letters = new Set(myArray);
let size = letters.size;
size = 3Creates a new Map
const fruits = new Map();Sets the value for a key in a Map
const preMap = new Map();
for (let [crs, pre] of prerequisites) {
preMap.set(crs, (preMap.get(crs) || []).concat(pre));
}Gets the value for a key in a Map
const fruits = new Map();
// Set Map Values
fruits.set("apples", 500);
fruits.get("apples"); // Returns 500Removes a Map element specified by the key
fruits.delete("apples");Returns true if a key exists in a Map
fruits.has("apples");How to iterate through a hashmap
for(let [key, val] of preMap) {
console.log(key);
console.log(val);
}Returns the number of elements in a Map
console.log(fruits.size);Find Intersection of Two Arrays
Input: nums1 = [4,9,5], nums2 = [9,4,9,8,4]
Output: [9,4]
Explanation: [4,9] is also accepted.
const set_intersection = (set1, set2) => {
let output = [];
const arr = Array.from(set1)
for (let s of arr)
if (set2.has(s)) {
output.push(s);
}
return output;
}
var intersection = function(nums1, nums2) {
let set1 = new Set(nums1);
let set2 = new Set(nums2);
if (set1.size < set2.size) {
return set_intersection(set1, set2);
}
else {
return set_intersection(set2, set1);
}
};The pop() method removes the last element from an array:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.pop();
fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple"]const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
let fruit = fruits.pop();
fruit = "Mango"The push() method adds a new element to an array (at the end):
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.push("Kiwi");
fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango", "Kiwi"];The shift() method removes the first array element and "shifts" all other elements to a lower index.
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.shift();
fruits = ["Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];The unshift() method adds a new element to an array (at the beginning), and "unshifts" older elements:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.unshift("Lemon");
fruits = ["Lemon","Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];The concat() method creates a new array by merging (concatenating) existing arrays:
const myGirls = ["Cecilie", "Lone"];
const myBoys = ["Emil", "Tobias", "Linus"];
const myChildren = myGirls.concat(myBoys);
myChildren = Cecilie,Lone,Emil,Tobias,LinusThe splice() method adds new items to an array.
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.splice(2, 0, "Lemon", "Kiwi");
fruits = Banana, Orange, Lemon, Kiwi, Apple, Mango
//The first parameter (2) defines the position where new elements should be added (spliced in).
//The second parameter (0) defines how many elements should be removed.
//The rest of the parameters ("Lemon" , "Kiwi") define the new elements to be added.The slice() method slices out a piece of an array.
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Lemon", "Apple", "Mango"];
const citrus = fruits.slice(1);
//This example slices out a part of an array starting from array element 1 ("Orange")
fruits = Orange, Lemon, Apple, MangoCreate an array from 0 to N
[...Array(10).keys()]slice() extracts a part of a string and returns the extracted part in a new string.
The method takes 2 parameters: start position, and end position (end not included).
let text = "Apple, Banana, Kiwi";
let part = text.slice(7, 13);
return Bananalet text = "Apple, Banana, Kiwi";
let part = text.slice(7);
return Banana, KiwiThe indexOf() method returns the index of (position of) the first occurrence of a string in a string:
let str = "Please locate where 'locate' occurs!";
str.indexOf("locate");
return 7Break string into Array
let text = "How are you doing today?";
const myArray = text.split(" ");
Output: ["How","are","you","doing","today?"]Remove the first and last char of a string
let str = "Hello";
let newStr = str.slice(1,-1);
console.log(newStr);
Output: "ell"Find the interesection between 2 strings
let arr1 = ["a","b];
let arr2 = ["b","a","d"];
let filtered = arr1.filter(c => arr2.includes(c));
console.log(filtered);
Output: ["a","b"]
Write a function that takes an unsigned integer and returns the number of '1' bits it has.
Input: n = 00000000000000000000000000001011
Output: 3
Explanation: The input binary string 00000000000000000000000000001011 has a total of three '1' bits.
var hammingWeight = function(n) {
let count = 0;
while (n !== 0) {
let bitComp = n & 1; //1 &1 will return 1, 0 &1 will return 0
if (bitComp === 1) count++;
n >>>= 1; // unsigned right shift assignment (chop off the last bit and assign it)
}
return count;
};


O(1):
push and pop of stack/array
O(n):
Traversing an array
Linear search
O(log n):
O(log n) can be faster than O(n) on large data set.
Binary search
O(n log n):
Divide and Conquer Algorithms
O(n2):
Traversing 2D array
O(n!):
Generating all unrestricted permutations of a partially ordered set