| Type | Bootloader | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ISO | netboot.xyz.iso | Used for CD/DVD, Virtual CDs, DRAC/iLO, VMware, Virtual Box |
| USB | netboot.xyz.usb | Used for creation of USB Keys |
| Kernel | netboot.xyz.lkrn | Used for booting from GRUB/EXTLINUX |
| Floppy | netboot.xyz.dsk | Virtual floppy disk for DRAC/iLO, VMware, Virtual Box, etc |
| DHCP | netboot.xyz.kpxe | DHCP boot image file, uses built-in iPXE NIC drivers |
| DHCP-undionly | netboot.xyz-undionly.kpxe | DHCP boot image file, use if you have NIC issues |
| Type | Bootloader | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ISO | netboot.xyz-efi.iso | Used for CD/DVD, Virtual CDs, DRAC/iLO, VMware, Virtual Box |
| USB | netboot.xyz-efi.usb | Used for creation of USB Keys |
| DHCP | netboot.xyz.efi | DHCP boot image file, uses built-in iPXE NIC drivers |
| DHCP-snp | netboot.xyz-snp.efi | EFI w/ Simple Network Protocol, attempts to boot all net devices |
| DHCP-snponly | netboot.xyz-snponly.efi | EFI w/ Simple Network Protocol, only boots from device chained from |
SHA256 checksums are generated during each build of iPXE and are located here. You can also view the scripts that are embedded into the images here.
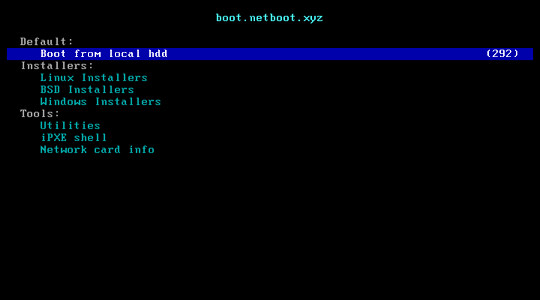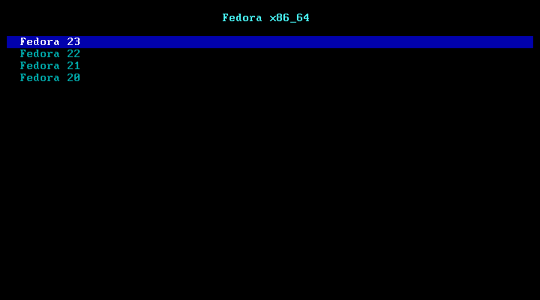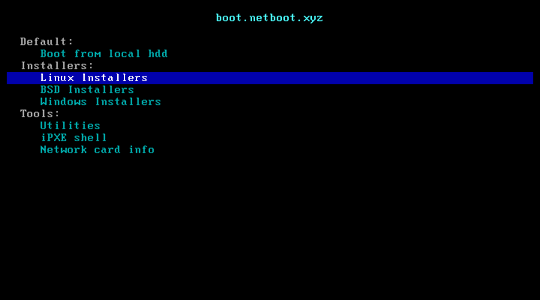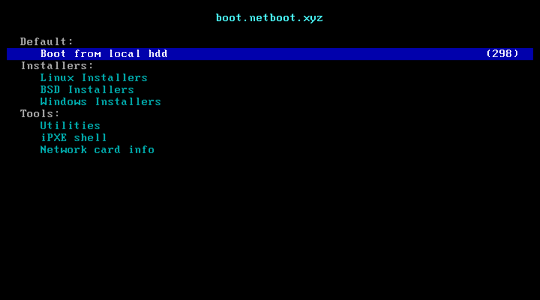
netboot.xyz is a convenient place to boot into any type of operating system or utility disk without the need of having to go spend time retrieving the ISO just to run it. iPXE is used to provide a user friendly menu from within the BIOS that lets you easily choose the operating system you want along with any specific types of versions or bootable flags.
If you already have iPXE up and running on the network, you can hit netboot.xyz at anytime by typing:
chain --autofree https://boot.netboot.xyz/ipxe/netboot.xyz.lkrn
or when in EFI mode:
chain --autofree https://boot.netboot.xyz/ipxe/netboot.xyz.efi
This will load the appropriate netboot.xyz kernel with all of the proper options enabled.
See netboot.xyz for all documentation. Some links to get started with are:
If you'd like to contribute to the documentation, the netboot.xyz documentation is located at netboot.xyz-docs.
For those users who want to deploy their own netboot.xyz environment, you can leverage the same scripts that are used to deploy the hosted environment. The source scripts are all Ansible templates and can be generated and customized to your preference.
Please see the self-hosting docs for more information but in short:
To generate, run:
ansible-playbook -i inventory site.yml
The build output will be located in /var/www/html by default.
docker build -t localbuild -f Dockerfile-build .
docker run --rm -it -v $(pwd):/buildout localbuild
The build output will be in the generated folder buildout
Ansible will handle source generation as well as iPXE disk generation with your settings. It will generate Legacy (PCBIOS) and UEFI iPXE disks that can be used to load into your netboot.xyz environment. If you want to override the defaults, you can put overrides in user_overrides.yml. See user_overrides.yml for examples.
Using the overrides file, you can override all of the settings from the defaults/main.yml so that you can easily change the boot mirror URLs when the menus are rendered. If you prefer to do this after the fact, you can also edit the boot.cfg to make changes, but keep in mind those changes will not be saved when you redeploy the menu.
In addition to being able to host netboot.xyz locally, you can also create your own custom templates for custom menus within netboot.xyz. Please see Custom User Menus for more information.
| Name | URL | Installer Kernel | Live OS |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALT Linux Rescue | https://en.altlinux.org/Rescue | ISO - Memdisk | - |
| Breakin | http://www.advancedclustering.com/products/software/breakin/ | Yes | Yes |
| Clonezilla | http://www.clonezilla.org/ | - | Yes |
| DBAN | http://www.dban.org/ | Yes | Yes |
| GParted | http://gparted.org | ISO - Memdisk | - |
| Grml | http://grml.org | ISO - Memdisk | - |
| Memtest | http://www.memtest.org/ | Yes | - |
| Super Grub2 Disk | http://www.supergrubdisk.org | ISO - Memdisk | - |
| Ultimate Boot CD | http://www.ultimatebootcd.com | ISO - Memdisk | - |
Feel free to open up an issue on Github or ping us on Discord. Follow us on Twitter and like us on Facebook!