Given an m x n board of characters and a list of strings words, return all words on the board.
Each word must be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once in a word.
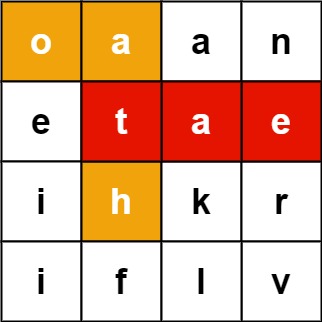
Input: board = [["o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v"]], words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"] Output: ["eat","oath"]
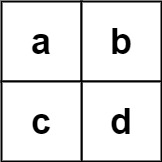
Input: board = [["a","b"],["c","d"]], words = ["abcb"] Output: []
m == board.lengthn == board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 12board[i][j]is a lowercase English letter.1 <= words.length <= 3 * 1041 <= words[i].length <= 10words[i]consists of lowercase English letters.- All the strings of
wordsare unique.
class Solution:
def findWords(self, board: List[List[str]], words: List[str]) -> List[str]:
def dfs(i: int, j: int, root: dict) -> None:
if (i, j) in visited or i < 0 or i >= m or j < 0 or j >= n or board[i][j] not in root:
return None
if root[board[i][j]][0] != "":
ret.append(root[board[i][j]][0])
root[board[i][j]][0] = ""
visited.add((i, j))
dfs(i - 1, j, root[board[i][j]][1])
dfs(i + 1, j, root[board[i][j]][1])
dfs(i, j - 1, root[board[i][j]][1])
dfs(i, j + 1, root[board[i][j]][1])
visited.remove((i, j))
m, n = len(board), len(board[0])
root = {}
visited = set()
ret = []
for word in words:
curr = root
for i, c in enumerate(word):
if c not in curr:
curr[c] = ["", {}]
if i == len(word) - 1:
curr[c][0] = word
curr = curr[c][1]
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
dfs(i, j, root)
return ret