|
| 1 | +# 概述 |
| 2 | +shortest_path_demo.py是一个基于 OxyGent 框架的多代理系统并且专注于网络最短路径计算与优化的示例,结合Google OR-Tools的求解能力与JoyCode的编码能力共同构建。该系统能够高效地解决各种网络拓扑中的最短路径问题,特别适用于通信网络、交通路线规划等场景。系统支持从Excel/CSV文件导入网络拓扑数据,计算指定节点间的最短路径,并提供可视化展示功能。 |
| 3 | +# 核心功能 |
| 4 | +- **多智能体系统**:基于oxygent框架实现的多智能体协作系统 |
| 5 | +- **最短路径计算**:基于Google OR-Tools的min_cost_flow算法实现高效的最短路径计算 |
| 6 | +- **网络数据导入**:支持从Excel/CSV文件导入网络拓扑数据 |
| 7 | +- **路径可视化**:使用matplotlib和networkx生成网络拓扑图和最短路径可视化 |
| 8 | +# 核心组件 |
| 9 | +1. 最短路径算法模块 (shortest_path.py) |
| 10 | + - 基于Google OR-Tools的min_cost_flow实现 |
| 11 | + - 支持基本最短路径、城市间最短路径和带约束的最短路径计算 |
| 12 | + - 提供路径可视化功能 |
| 13 | +2. 智能体配置 (shortest_path_demo.py) |
| 14 | + - 配置多智能体系统 |
| 15 | + - 设置LLM模型连接 |
| 16 | + - 启动应用 |
| 17 | +# 技术栈 |
| 18 | +**Python**:核心编程语言 |
| 19 | +**Google OR-Tools**:提供最短路径算法实现 |
| 20 | +**Oxygent**:多智能体系统框架 |
| 21 | +**Pandas**:数据处理和Excel文件读取 |
| 22 | +**Matplotlib & NetworkX**:网络可视化 |
| 23 | + |
| 24 | +# 数据模型 |
| 25 | +系统处理的网络拓扑数据主要包含以下字段: |
| 26 | +cities:节点/城市名称列表 |
| 27 | +start_cities:边的起始节点 |
| 28 | +end_cities:边的终止节点 |
| 29 | +distances:边的距离/权重 |
| 30 | +costs:边的成本(可选) |
| 31 | +如表格图片所示,一个网络拓扑例子(NSFNET) |
| 32 | +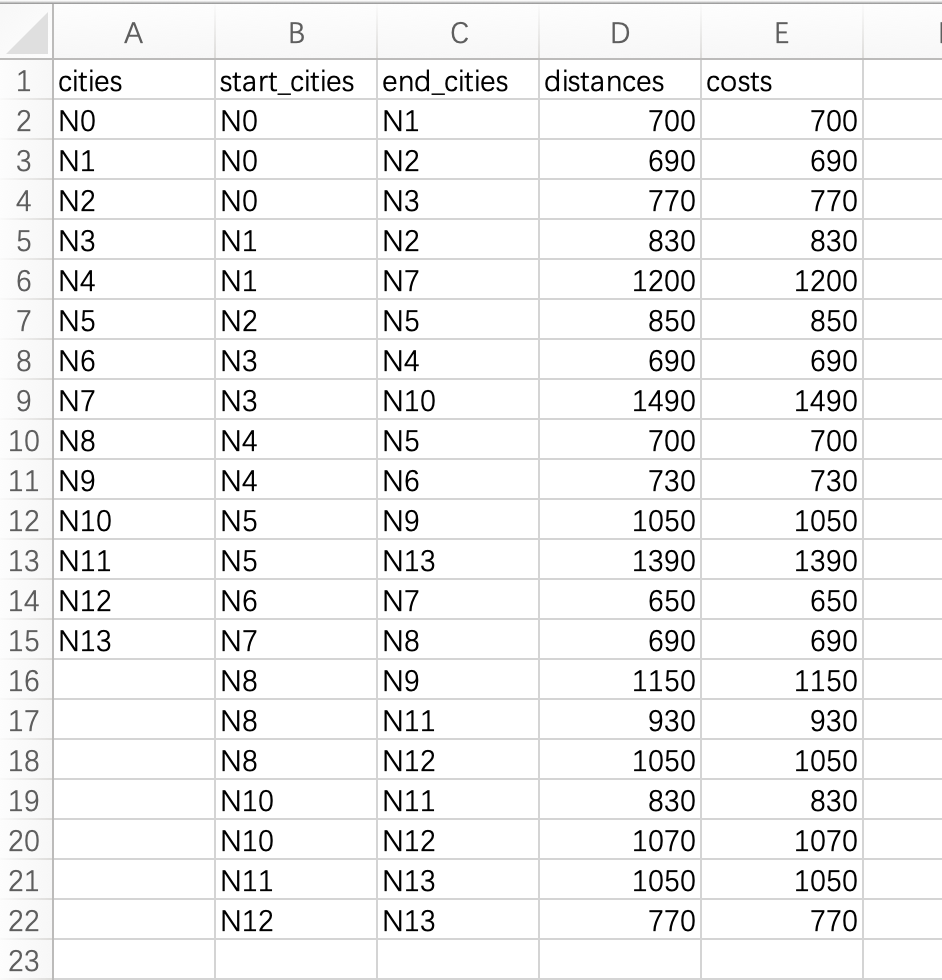 |
| 33 | +# 实现细节 |
| 34 | +## 最短路径算法与可视化 |
| 35 | +目前,最短路径算法实现的方案较多,启发式、线性规划等,这里基于Google OR-Tools的min_cost_flow方法实现最短路径的精确求解。此外,shortest_path.py 是一个工具文件,目的是为了在OxyGent中注册为Agent可以随时调用的工具,因此,shortest_path.py主要包含以下功能: |
| 36 | +**数据导入功能**:info_update()函数从Excel文件读取网络拓扑数据 |
| 37 | +```python |
| 38 | +@shortest_path_tools.tool(description="根据excel更新cityies和distances信息") |
| 39 | +async def info_update(file_path, sheet_name=0): |
| 40 | + # 读取 Excel 文件 |
| 41 | + df = pd.read_excel(file_path, sheet_name=sheet_name) |
| 42 | + print(df) |
| 43 | + |
| 44 | + # 遍历数据框中的每一列 |
| 45 | + for column in df.columns: |
| 46 | + # 将每一列的数据存储到列表中 |
| 47 | + column_data[column] = df[column].dropna().tolist() |
| 48 | + |
| 49 | + print(column_data) |
| 50 | +``` |
| 51 | +**最短路径计算**:shortest_path()函数计算指定起点和终点间的最短路径 |
| 52 | +```python |
| 53 | +@shortest_path_tools.tool(description="A tool that can calculate the shortest path between different points") |
| 54 | +async def shortest_path(start_city: str, end_city): |
| 55 | + # 城市列表 |
| 56 | + city_to_index = {city: i for i, city in enumerate(column_data['cities'])} |
| 57 | + print(start_city, end_city) |
| 58 | + |
| 59 | + cities = column_data['cities'] |
| 60 | + start_cities = column_data['start_cities'] |
| 61 | + end_cities = column_data['end_cities'] |
| 62 | + distances = column_data['distances'] |
| 63 | + # 转换城市名称为索引 |
| 64 | + start_nodes = [city_to_index[city] for city in start_cities] |
| 65 | + end_nodes = [city_to_index[city] for city in end_cities] |
| 66 | + # 创建有向图求解器 |
| 67 | + sp_func = min_cost_flow.SimpleMinCostFlow() |
| 68 | + |
| 69 | + # 添加每条边到图中 (注意:我们需要添加双向边,因为城市之间的道路是双向的) |
| 70 | + for i in range(len(start_nodes)): |
| 71 | + sp_func.add_arc_with_capacity_and_unit_cost( |
| 72 | + start_nodes[i], end_nodes[i], 1, distances[i]) |
| 73 | + sp_func.add_arc_with_capacity_and_unit_cost( |
| 74 | + end_nodes[i], start_nodes[i], 1, distances[i]) |
| 75 | + |
| 76 | + # 设置起点和终点的供应/需求 |
| 77 | + sp_func.set_node_supply(city_to_index[start_city], 1) # 起点 |
| 78 | + sp_func.set_node_supply(city_to_index[end_city], -1) # 终点 |
| 79 | + |
| 80 | + # 求解最短路径 |
| 81 | + start_time = time.time() |
| 82 | + status = sp_func.solve() |
| 83 | + end_time = time.time() |
| 84 | + |
| 85 | + # 构建结果 |
| 86 | + result = {} |
| 87 | + if status == min_cost_flow.SimpleMinCostFlow.OPTIMAL: |
| 88 | + result["status"] = "optimal" |
| 89 | + result["distance"] = sp_func.optimal_cost() |
| 90 | + result["solve_time"] = end_time - start_time |
| 91 | + |
| 92 | + # 遍历所有边,找出流量为 1 的边(即最短路径上的边) |
| 93 | + path = [] |
| 94 | + path_cities = [] |
| 95 | + for i in range(sp_func.num_arcs()): |
| 96 | + if sp_func.flow(i) > 0: |
| 97 | + tail = sp_func.tail(i) |
| 98 | + head = sp_func.head(i) |
| 99 | + path.append((tail, head)) |
| 100 | + path_cities.append(f"{cities[tail]} -> {cities[head]}") |
| 101 | + |
| 102 | + result["path"] = path |
| 103 | + result["path_cities"] = path_cities |
| 104 | + # 可视化城市路径 |
| 105 | + visualize_city_path(cities, start_cities, end_cities, distances, path) |
| 106 | + else: |
| 107 | + result["status"] = "not_optimal" |
| 108 | + |
| 109 | + return result |
| 110 | +``` |
| 111 | +**路径可视化**:visualize_city_path()函数生成网络拓扑和路径的可视化图像 |
| 112 | +```python |
| 113 | +def visualize_city_path(cities, start_cities, end_cities, distances, path): |
| 114 | + """ |
| 115 | + 可视化城市图和最短路径 |
| 116 | + 参数: |
| 117 | + cities: 城市列表 |
| 118 | + start_cities: 起始城市列表 |
| 119 | + end_cities: 终止城市列表 |
| 120 | + distances: 距离列表 |
| 121 | + path: 最短路径上的边列表 (使用城市索引) |
| 122 | + """ |
| 123 | + try: |
| 124 | + # 创建图 |
| 125 | + G = nx.Graph() |
| 126 | + # 添加节点 |
| 127 | + for city in cities: |
| 128 | + G.add_node(city) |
| 129 | + # 添加边和权重 |
| 130 | + for i in range(len(start_cities)): |
| 131 | + G.add_edge(start_cities[i], end_cities[i], weight=distances[i]) |
| 132 | + |
| 133 | + # 创建位置字典 |
| 134 | + city_positions = nx.spring_layout(G, seed=42) |
| 135 | + # 绘制图 |
| 136 | + plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10)) |
| 137 | + # 绘制所有边 |
| 138 | + nx.draw_networkx_edges(G, city_positions, alpha=0.3, width=1) |
| 139 | + # 高亮显示最短路径上的边 |
| 140 | + path_edges = [] |
| 141 | + for u, v in path: |
| 142 | + path_edges.append((cities[u], cities[v])) |
| 143 | + nx.draw_networkx_edges(G, city_positions, edgelist=path_edges, width=3, edge_color='r') |
| 144 | + # 绘制节点 |
| 145 | + nx.draw_networkx_nodes(G, city_positions, node_size=700, node_color='lightblue') |
| 146 | + # 绘制节点标签 |
| 147 | + nx.draw_networkx_labels(G, city_positions, font_size=12, font_family='SimHei') |
| 148 | + # 绘制边权重 |
| 149 | + edge_labels = nx.get_edge_attributes(G, 'weight') |
| 150 | + nx.draw_networkx_edge_labels(G, city_positions, edge_labels=edge_labels, font_size=8) |
| 151 | + |
| 152 | + plt.title("中国城市间最短路径", fontsize=16, fontfamily='SimHei') |
| 153 | + plt.axis('off') |
| 154 | + plt.tight_layout() |
| 155 | + plt.savefig("city_shortest_path.png") |
| 156 | + print("\n城市路径图已保存为 'city_shortest_path.png'") |
| 157 | + except Exception as e: |
| 158 | + print(f"可视化过程中出错: {e}") |
| 159 | + print("跳过可视化步骤...") |
| 160 | + |
| 161 | +``` |
| 162 | + |
| 163 | +## 智能体配置 |
| 164 | +需要了解OxyGent如何使用的同学可以参考这篇神灯文章:[使用Ollama服务本地启动OxyGent演示案例](http://xingyun.jd.com/shendeng/article/detail/52491?forumId=0&jdme_router=jdme://web/202206081297?url%3Dhttp%3A%2F%2Fsd.jd.com%2Farticle%2F52491)。这里不再赘述OxyGent的配置方法。本示例使用了三个agent,分别为: |
| 165 | +- **shortest_path_agent**:负责最短路径计算。 |
| 166 | +- **excel_agent**:负责excel文件读取操作,并且更新信息。 |
| 167 | +- **master_agent**:作为主控智能体协调其他智能体。 |
| 168 | +核心代码如下: |
| 169 | +```python |
| 170 | +import os |
| 171 | +from oxygent import MAS, Config, oxy, preset_tools |
| 172 | +from tools.shortest_path import shortest_path_tools |
| 173 | + |
| 174 | +## 注册LLM地址 |
| 175 | +Config.set_agent_llm_model("default_llm") |
| 176 | + |
| 177 | +## 创建最短路径计算智能体 |
| 178 | +def create_optimal_agent(): |
| 179 | + return oxy.ReActAgent( |
| 180 | + name="shortest_path_agent", |
| 181 | + desc="Agent for computing shortest path between different cities", |
| 182 | + category="agent", |
| 183 | + class_name="ReActAgent", |
| 184 | + tools=["shortest_path_tools"], |
| 185 | + llm_model="default_llm", |
| 186 | + is_entrance=False, |
| 187 | + is_permission_required=False, |
| 188 | + is_save_data=True, |
| 189 | + timeout=30, |
| 190 | + retries=3, |
| 191 | + delay=1, |
| 192 | + is_multimodal_supported=False, |
| 193 | + semaphore=2, |
| 194 | + ) |
| 195 | +## 注册智能体 |
| 196 | +oxy_space = [ |
| 197 | + oxy.HttpLLM( |
| 198 | + name="default_llm", |
| 199 | + api_key=os.getenv("DEFAULT_LLM_API_KEY"), |
| 200 | + base_url=os.getenv("DEFAULT_LLM_BASE_URL"), |
| 201 | + model_name=os.getenv("DEFAULT_LLM_MODEL_NAME"), |
| 202 | + ), |
| 203 | + shortest_path_tools, |
| 204 | + create_optimal_agent(), |
| 205 | + oxy.ReActAgent( |
| 206 | + name="excel_agent", |
| 207 | + desc="A tool that can operate the file system", |
| 208 | + tools=["shortest_path_tools"], |
| 209 | + ), |
| 210 | + oxy.ReActAgent( |
| 211 | + is_master=True, |
| 212 | + name="master_agent", |
| 213 | + sub_agents=["excel_agent","shortest_path_agent"], |
| 214 | + ), |
| 215 | +] |
| 216 | +## web启动 |
| 217 | +async def main(): |
| 218 | + async with MAS(oxy_space=oxy_space) as mas: |
| 219 | + await mas.start_web_service(first_query="What is the shortest path between N0 and N3 now?") |
| 220 | + |
| 221 | +if __name__ == "__main__": |
| 222 | + import asyncio |
| 223 | + asyncio.run(main()) |
| 224 | +``` |
| 225 | +# 示例 |
| 226 | +启动应用:**python shortest_path_demo.py** |
| 227 | +使用的网络是是美国骨干网络拓扑USnet,包含24个节点(N0-N23),43条边连接。如下图所示,excel_agent读取在usnet.xlsx文件并且更新节点和网络路径信息。 |
| 228 | +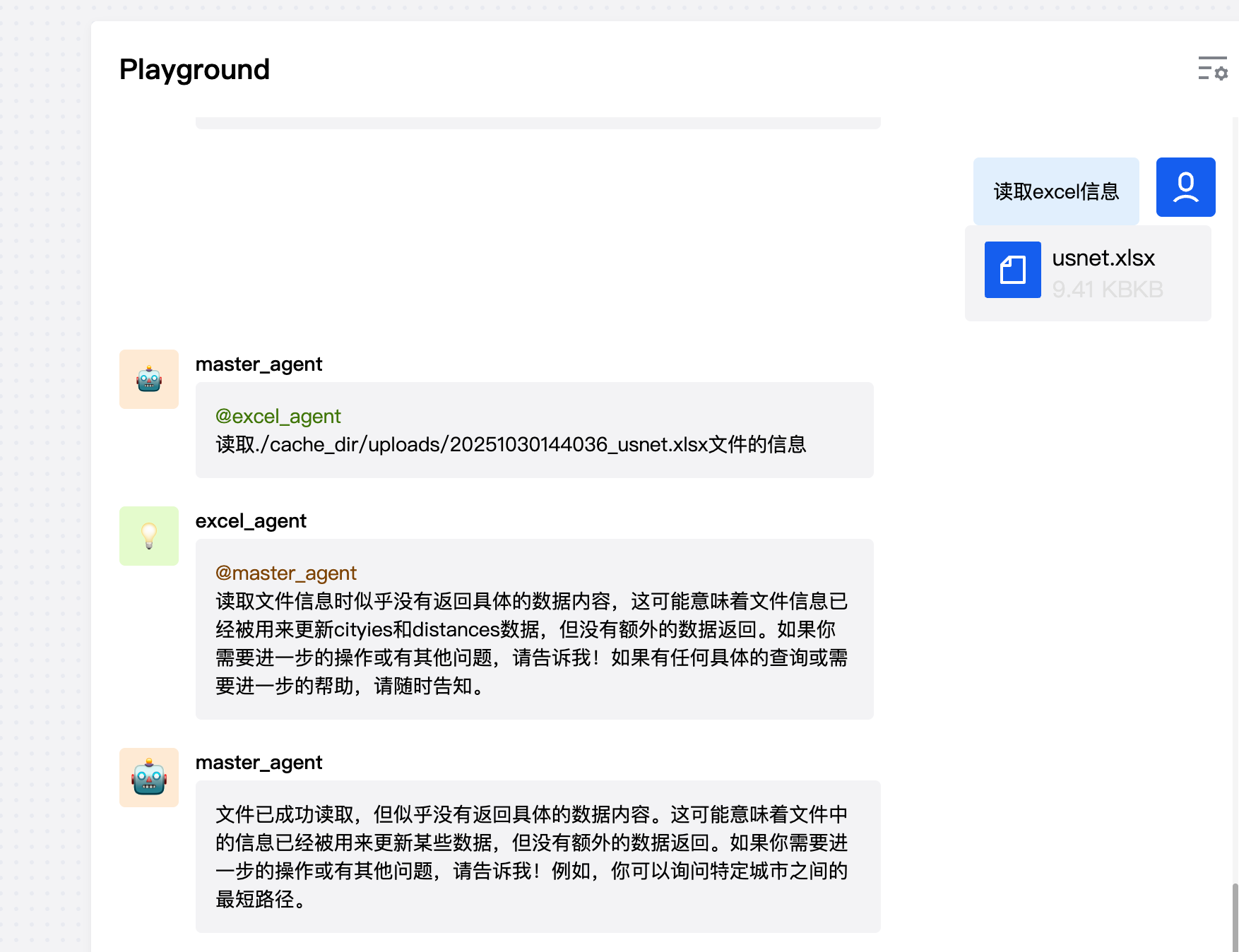 |
| 229 | +获取网络信息后,可以通过人为询问的方式获取两个节点之间的最短路径。 |
| 230 | + |
| 231 | +同时,在项目的文件夹下,也会生成对应的最短路径图。 |
| 232 | +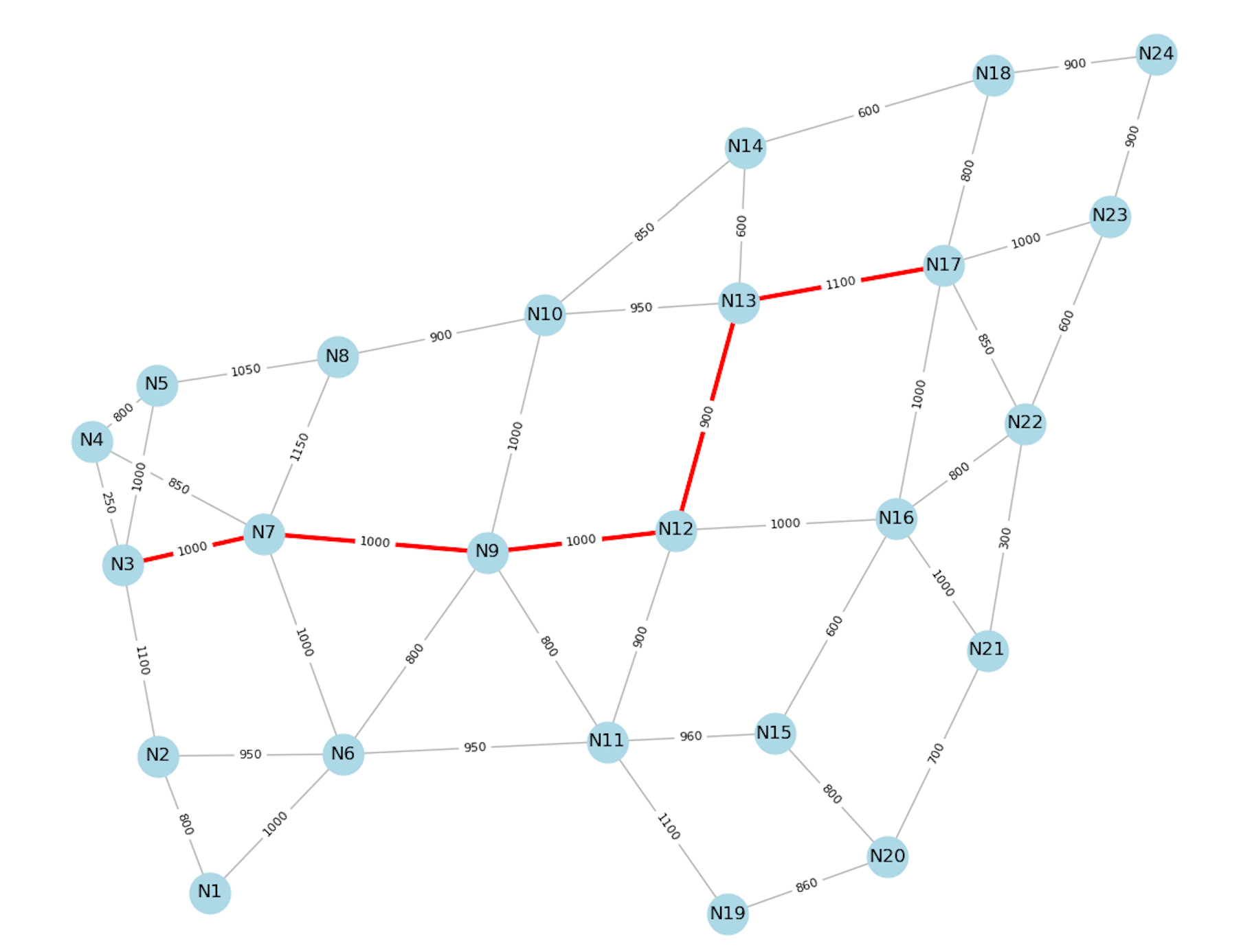 |
| 233 | + |
| 234 | + |
| 235 | +# 总结 |
| 236 | +OxyGent结合JoyCode的高效开发为大模型的应用提供了更多可能性。基于不同能力需求,用户可以随时打造出自己的千军万马!**shortest_path_demo**提供一个简单的应用场景示例,现实优化场景可能会面临较多限制与不确定因素,在大模型的辅助下,可最大化帮助开发人员简化问题难度,并降低操作学习成本。 |
0 commit comments