| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
2460 |
Biweekly Contest 89 Q4 |
|
There is an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1.
You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums of length n where nums[i] represents the value of the ith node. You are also given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1 where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
You are allowed to delete some edges, splitting the tree into multiple connected components. Let the value of a component be the sum of all nums[i] for which node i is in the component.
Return the maximum number of edges you can delete, such that every connected component in the tree has the same value.
Example 1:
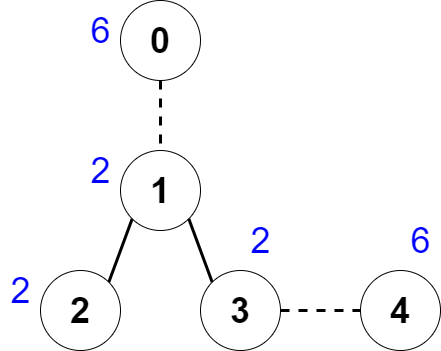
Input: nums = [6,2,2,2,6], edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3],[3,4]] Output: 2 Explanation: The above figure shows how we can delete the edges [0,1] and [3,4]. The created components are nodes [0], [1,2,3] and [4]. The sum of the values in each component equals 6. It can be proven that no better deletion exists, so the answer is 2.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2], edges = [] Output: 0 Explanation: There are no edges to be deleted.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 2 * 104nums.length == n1 <= nums[i] <= 50edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= edges[i][0], edges[i][1] <= n - 1edgesrepresents a valid tree.
Assume the number of connected blocks is
We enumerate
The key point is to judge whether for a given
Here we use the dfs function to judge. We recursively traverse from top to bottom to calculate the value of each subtree. If the sum of the subtree values is exactly
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def componentValue(self, nums: List[int], edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def dfs(i, fa):
x = nums[i]
for j in g[i]:
if j != fa:
y = dfs(j, i)
if y == -1:
return -1
x += y
if x > t:
return -1
return x if x < t else 0
n = len(nums)
g = defaultdict(list)
for a, b in edges:
g[a].append(b)
g[b].append(a)
s = sum(nums)
mx = max(nums)
for k in range(min(n, s // mx), 1, -1):
if s % k == 0:
t = s // k
if dfs(0, -1) == 0:
return k - 1
return 0class Solution {
private List<Integer>[] g;
private int[] nums;
private int t;
public int componentValue(int[] nums, int[][] edges) {
int n = nums.length;
g = new List[n];
this.nums = nums;
Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
for (var e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
g[a].add(b);
g[b].add(a);
}
int s = sum(nums), mx = max(nums);
for (int k = Math.min(n, s / mx); k > 1; --k) {
if (s % k == 0) {
t = s / k;
if (dfs(0, -1) == 0) {
return k - 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
private int dfs(int i, int fa) {
int x = nums[i];
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (j != fa) {
int y = dfs(j, i);
if (y == -1) {
return -1;
}
x += y;
}
}
if (x > t) {
return -1;
}
return x < t ? x : 0;
}
private int sum(int[] arr) {
int x = 0;
for (int v : arr) {
x += v;
}
return x;
}
private int max(int[] arr) {
int x = arr[0];
for (int v : arr) {
x = Math.max(x, v);
}
return x;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int componentValue(vector<int>& nums, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
int n = nums.size();
int s = accumulate(nums.begin(), nums.end(), 0);
int mx = *max_element(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int t = 0;
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> g;
for (auto& e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
g[a].push_back(b);
g[b].push_back(a);
}
function<int(int, int)> dfs = [&](int i, int fa) -> int {
int x = nums[i];
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (j != fa) {
int y = dfs(j, i);
if (y == -1) return -1;
x += y;
}
}
if (x > t) return -1;
return x < t ? x : 0;
};
for (int k = min(n, s / mx); k > 1; --k) {
if (s % k == 0) {
t = s / k;
if (dfs(0, -1) == 0) {
return k - 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
};func componentValue(nums []int, edges [][]int) int {
s, mx := 0, slices.Max(nums)
for _, x := range nums {
s += x
}
n := len(nums)
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
a, b := e[0], e[1]
g[a] = append(g[a], b)
g[b] = append(g[b], a)
}
t := 0
var dfs func(int, int) int
dfs = func(i, fa int) int {
x := nums[i]
for _, j := range g[i] {
if j != fa {
y := dfs(j, i)
if y == -1 {
return -1
}
x += y
}
}
if x > t {
return -1
}
if x < t {
return x
}
return 0
}
for k := min(n, s/mx); k > 1; k-- {
if s%k == 0 {
t = s / k
if dfs(0, -1) == 0 {
return k - 1
}
}
}
return 0
}