dbt is an open source project to build data transformation pipelines with supported databases such as BigQuery, Postgres, Redshift and more.
In this sample, I want to show you how to setup a scheduled Cloud Run service that uses dbt with BigQuery backend.
I'm assuming that you already have a Google Cloud project setup with BigQuery
enabled, you have gcloud setup to use that project and you have dbt
installed locally.
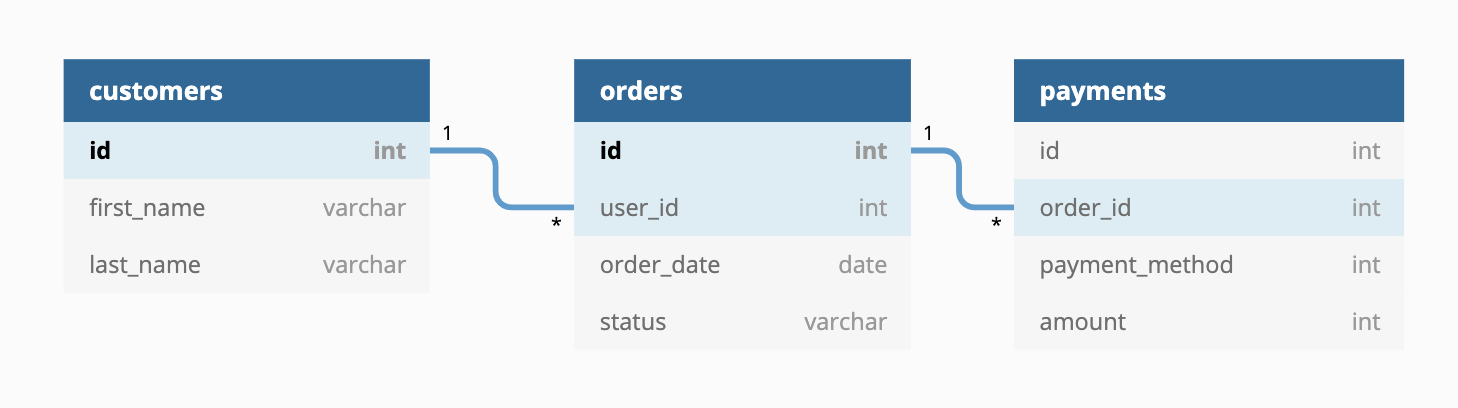
For the sample dbt service, we will use
jaffle-shop. jaffle_shop
is a fictional ecommerce store with the following tables:
There is already a public project dbt-tutorial with a jaffle_shop dataset
in BigQuery:
There is also a tutorial in DBT documentation showing how to transform this dataset with DBT. We will transform this tutorial into a scheduled service.
We already setup the sample project in jaffle-shop folder. Feel free to explore it in detail. We'll highlight a few things.
First, dbt_project.yml file has jaffle_shop name and
profile. It also has a single jaffle_shop model materialized as table.
Second, profiles.yml defines the BigQuery backend for dbt to connect to. This profile uses oauth for authentication to create a BigQuery dataset in your project.
Third, customers.sql defines the
model for dbt. It reads from dbt-tutorial project's jaffle_shop dataset and
creates a new transformed customers table.
Run dbt with this new profile:
$ dbt run --profiles-dir .
Running with dbt=0.17.2
Found 1 model, 0 tests, 0 snapshots, 0 analyses, 147 macros, 0 operations, 0 seed files, 0 sources
16:16:10 | Concurrency: 1 threads (target='dev')
16:16:10 |
16:16:10 | 1 of 1 START table model dbt_atamel_dataset.customers................ [RUN]
16:16:15 | 1 of 1 OK created table model dbt_atamel_dataset.customers........... [CREATE TABLE (100) in 4.84s]
16:16:15 |
16:16:15 | Finished running 1 table model in 9.96s.
Completed successfully
Done. PASS=1 WARN=0 ERROR=0 SKIP=0 TOTAL=1You should see a new dataset and a customers table created in BigQuery:
Running dbt on Cloud Run has a few challenges, namely:
- dbt is mainly a command line tool whereas Cloud Run expects HTTP requests. How do you call dbt command from a Cloud Run service?
- Cloud Run runs containers. How do you run dbt in a container?
- How do you authenticate dbt with BigQuery? OAuth works for end users but for services running in the cloud, it's probably not the right solution.
For #1, Cloud Run has an example on how to run a shell command from an HTTP Server deployed to Cloud Run. It involves setting up a Go based HTTP server that simply calls a shell script upon receiving a GET request. You can simply copy that as invoke.go. In our case, the shell script, script.sh calls dbt with the profile folder.
For #2, dbt has some base images that you can rely on (although the documentation is pretty much non-existent). This is a sample Dockerfile that works:
FROM golang:1.13 as builder
WORKDIR /app
COPY invoke.go ./
RUN CGO_ENABLED=0 GOOS=linux go build -v -o server
FROM fishtownanalytics/dbt:0.17.0
USER root
WORKDIR /dbt
COPY --from=builder /app/server ./
COPY script.sh ./
COPY jaffle-shop ./
ENTRYPOINT "./server"In this Dockerfile, we first build the HTTP server. Then, we use the dbt base image, copy our dbt project and also the script to call that project with the profile. Finally, we start the HTTP server to receive requests.
For #3, Cloud Run, by default, uses the Compute Engine default service account and that should be able to make BigQuery calls. However, it's best practice to assign a more granular permission to your Cloud Run service by assigning a dedicated service account with more restricted IAM roles.
In this case, create a service account with bigquery.admin role (you probably
want to use even a finer grained role in production):
export SERVICE_ACCOUNT=dbt-sa
gcloud iam service-accounts create ${SERVICE_ACCOUNT} \
--display-name "DBT BigQuery Service Account"
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding \
$(gcloud config get-value project) \
--member=serviceAccount:${SERVICE_ACCOUNT}@$(gcloud config get-value project).iam.gserviceaccount.com \
--role=roles/bigquery.adminEnable the Cloud Build and Run APIs:
gcloud services enable run.googleapis.com
gcloud services enable cloudbuild.googleapis.comBuild the container:
export SERVICE_NAME=dbt-service
gcloud builds submit \
--tag gcr.io/$(gcloud config get-value project)/${SERVICE_NAME}Deploy to Cloud Run with the service account created earlier and also
no-allow-unauthenticated flag to make it a private service:
gcloud run deploy ${SERVICE_NAME} \
--image gcr.io/$(gcloud config get-value project)/${SERVICE_NAME} \
--service-account ${SERVICE_ACCOUNT}@$(gcloud config get-value project).iam.gserviceaccount.com \
--platform managed \
--no-allow-unauthenticatedThe final step is to call the Cloud Run service on a schedule. You can do this with Cloud Scheduler.
Enable the Cloud Scheduler API:
gcloud services enable cloudscheduler.googleapis.comCreate a service account for Cloud Scheduler with run.invoker role:
export SERVICE_ACCOUNT=dbt-scheduler-sa
gcloud iam service-accounts create ${SERVICE_ACCOUNT} \
--display-name "DBT Scheduler Service Account"
gcloud run services add-iam-policy-binding ${SERVICE_NAME} \
--member=serviceAccount:${SERVICE_ACCOUNT}@$(gcloud config get-value project).iam.gserviceaccount.com \
--role=roles/run.invoker \
--platform managedCreate a Cloud Scheduler job to call the service every 5 minutes:
export SERVICE_URL="$(gcloud run services list --platform managed --filter=${SERVICE_NAME} --format='value(URL)')"
gcloud scheduler jobs create http ${SERVICE_NAME}-job --schedule "*/5 * * * *" \
--http-method=GET \
--uri=${SERVICE_URL} \
--oidc-service-account-email=${SERVICE_ACCOUNT}@$(gcloud config get-value project).iam.gserviceaccount.com \
--oidc-token-audience=${SERVICE_URL}You can test that the service by manually invoking the job:
gcloud scheduler jobs run ${SERVICE_NAME}-jobAfter a few seconds, you should see the dataset created with a new customers table in BigQuery: