An implementation of the public-key encryption scheme NTRUEncrypt in C, following the IEEE P1363.1 standard.
NTRU's main strengths are high performance and resistance to quantum computer attacks. Its main drawback is that it is patent encumbered. The patents expire in 2021; when built with the NTRU_AVOID_HAMMING_WT_PATENT flag (see below), libntru becomes patent-free in 2017.
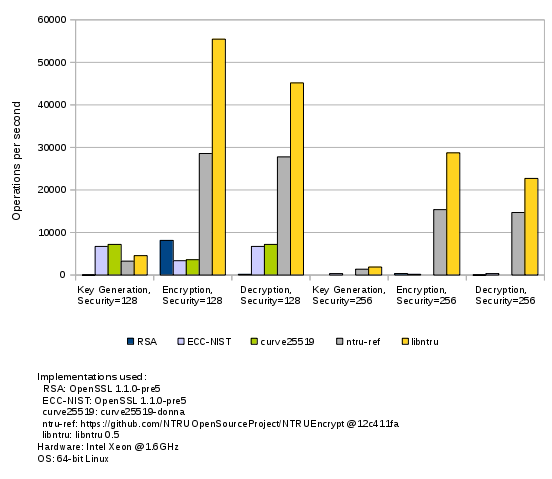
Benchmark results:
For more information on the NTRUEncrypt algorithm, see the NTRU introduction page at https://tbuktu.github.com/ntru/.
Run make to build the library, or make test to run unit tests. make bench builds a benchmark program.
On *BSD, use gmake instead of make.
The SSE environment variable enables SSSE3 support (SSE=yes)
or disables it (SSE=no).
Default on Linux, BSD, and MacOS is to autodetect SSSE3 on the build host,
Windows default is no SSSE3.
The AVX2 environment variable controls AVX2 support and works just like the SSE variable.
If the NTRU_AVOID_HAMMING_WT_PATENT preprocessor flag is supplied, the library won't support
parameter sets that will be patent encumbered after Aug 19, 2017. See the Parameter Sets section
for information on patent expiration dates.
#include "ntru.h"
/* key generation */
struct NtruEncParams params = NTRU_DEFAULT_PARAMS_128_BITS; /*see section "Parameter Sets" below*/
NtruRandGen rng_def = NTRU_RNG_DEFAULT;
NtruRandContext rand_ctx_def;
if (ntru_rand_init(&rand_ctx_def, &rng_def) != NTRU_SUCCESS)
printf("rng fail\n");
NtruEncKeyPair kp;
if (ntru_gen_key_pair(¶ms, &kp, &rand_ctx_def) != NTRU_SUCCESS)
printf("keygen fail\n");
/* deterministic key generation from password */
uint8_t seed[17];
strcpy(seed, "my test password");
NtruRandGen rng_ctr_drbg = NTRU_RNG_CTR_DRBG;
NtruRandContext rand_ctx_ctr_drbg;
if (ntru_rand_init_det(&rand_ctx_ctr_drbg, &rng_ctr_drbg, seed, strlen(seed)) != NTRU_SUCCESS)
printf("rng fail\n");
if (ntru_gen_key_pair(¶ms, &kp, &rand_ctx_ctr_drbg) != NTRU_SUCCESS)
printf("keygen fail\n");
/* encryption */
uint8_t msg[9];
strcpy(msg, "whatever");
uint8_t enc[ntru_enc_len(¶ms)];
if (ntru_encrypt(msg, strlen(msg), &kp.pub, ¶ms, &rand_ctx_def, enc) != NTRU_SUCCESS)
printf("encrypt fail\n");
/* decryption */
uint8_t dec[ntru_max_msg_len(¶ms)];
uint16_t dec_len;
if (ntru_decrypt((uint8_t*)&enc, &kp, ¶ms, (uint8_t*)&dec, &dec_len) != NTRU_SUCCESS)
printf("decrypt fail\n");
/* generate another public key for the existing private key */
NtruEncPubKey pub2;
if (ntru_gen_pub(¶ms, &kp.priv, &pub2, &rand_ctx_def) != NTRU_SUCCESS)
printf("pub key generation fail\n");
/* release RNG resources */
if (ntru_rand_release(&rand_ctx_def) != NTRU_SUCCESS)
printf("rng fail\n");
if (ntru_rand_release(&rand_ctx_ctr_drbg) != NTRU_SUCCESS)
printf("rng fail\n");
/* export key to uint8_t array */
uint8_t pub_arr[ntru_pub_len(¶ms)];
ntru_export_pub(&kp.pub, pub_arr);
/* import key from uint8_t array */
NtruEncPubKey pub;
ntru_import_pub(pub_arr, &pub);
For encryption of messages longer than ntru_max_msg_len(...), see src/hybrid.c
(requires OpenSSL lib+headers, use make hybrid to build).
| Name | Strength | Sizes (CText/Pub/Priv)1 | Enc / Dec Time2 | Pat. Until |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EES401EP1 | 112 bits | 552 / 556 / 264 | 2.5 / 2.7 | 8/19/2017 |
| EES541EP1 | 112 bits | 744 / 748 / 132 | 1.5 / 1.9 | 8/19/2017 |
| EES659EP1 | 112 bits | 907 / 911 / 104 | 1.5 / 2.0 | 8/19/2017 |
| EES401EP2 | 112 bits | 552 / 556 / 67 | 1.0 / 1.2 | 8/24/2021 |
| NTRU_DEFAULT_PARAMS_112_BITS | 112 bits | Synonym for EES401EP2 or EES401EP13 | ||
| EES449EP1 | 128 bits | 618 / 622 / 311 | 2.7 / 3.4 | 8/19/2017 |
| EES613EP1 | 128 bits | 843 / 847 / 147 | 1.6 / 2.2 | 8/19/2017 |
| EES761EP1 | 128 bits | 1047 / 1051 / 114 | 1.6 / 2.2 | 8/19/2017 |
| EES439EP1 | 128 bits | 604 / 608 / 68 | 1.1 / 1.4 | 8/24/2021 |
| EES443EP1 | 128 bits | 610 / 614 / 68 | 1.1 / 1.3 | 8/24/2021 |
| NTRU_DEFAULT_PARAMS_128_BITS | 128 bits | Synonym for EES443EP1 or EES449EP13 | ||
| EES677EP1 | 192 bits | 931 / 935 / 402 | 4.4 / 5.5 | 8/19/2017 |
| EES887EP1 | 192 bits | 1220 / 1224 / 212 | 2.8 / 3.9 | 8/19/2017 |
| EES1087EP1 | 192 bits | 1495 / 1499 / 183 | 3.0 / 4.0 | 8/19/2017 |
| EES593EP1 | 192 bits | 816 / 820 / 87 | 1.7 / 2.1 | 8/24/2021 |
| EES587EP1 | 192 bits | 808 / 812 / 87 | 1.9 / 2.3 | 8/24/2021 |
| NTRU_DEFAULT_PARAMS_192_BITS | 192 bits | Synonym for EES587EP1 or EES677EP13 | ||
| EES1087EP2 | 256 bits | 1495 / 1499 / 339 | 4.5 / 6.1 | 8/19/2017 |
| EES1171EP1 | 256 bits | 1611 / 1615 / 301 | 4.3 / 6.0 | 8/19/2017 |
| EES1499EP1 | 256 bits | 2062 / 2066 / 227 | 4.3 / 6.0 | 8/19/2017 |
| EES743EP1 | 256 bits | 1022 / 1026 / 111 | 2.2 / 2.9 | 8/24/2021 |
| NTRU_DEFAULT_PARAMS_256_BITS | 256 bits | Synonym for EES743EP1 or EES1087EP23 |
1 in bytes
2 relative to EES401EP2 encryption on a 1.6 GHz Intel Xeon
3 depending on the NTRU_AVOID_HAMMING_WT_PATENT flag
- Use NTRU_RNG_DEFAULT for non-deterministic keys and non-deterministic encryption
- Use NTRU_RNG_CTR_DRBG for deterministic keys and deterministic encryption
Other RNGs are NTRU_RNG_WINCRYPT, NTRU_RNG_DEVURANDOM, and NTRU_RNG_DEVRANDOM but these may be removed in a future release.
To use your own RNG, make an array of 3 function pointers: {init, generate, release} with the following signatures:
uint8_t init(NtruRandContext *rand_ctx, NtruRandGen *rand_gen);uint8_t generate(uint8_t rand_data[], uint16_t len, NtruRandContext *rand_ctx);uint8_t release(NtruRandContext *rand_ctx);
Ignore rand_ctx->seed in init() if your RNG is non-deterministic.
libntru has been tested on Linux, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, Mac OS X, and Windows (MingW).
- Wikipedia article: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NTRUEncrypt
- Original NTRUEncrypt paper: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.25.8422&rep=rep1&type=pdf
- Follow-up NTRUEncrypt paper: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.64.6834&rep=rep1&type=pdf
- NTRU articles (technical and mathematical): https://www.securityinnovation.com/products/encryption-libraries/ntru-crypto/ntru-resources.html
- EESS: http://grouper.ieee.org/groups/1363/lattPK/submissions/EESS1v2.pdf
- Jeffrey Hoffstein et al: An Introduction to Mathematical Cryptography, Springer-Verlag, ISBN 978-0-387-77993-5