-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 360
How to perform difference set operation on continuous intervals with esProc
There are two tables in a certain database. The original inventory table data_add stores multiple batches of inventory for multiple items. Each batch of inventory has a starting number START_NUM and an ending number END_NUM, representing the range of an interval.
| ID | ITEM_ID | START_NUM | END_NUM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 337 | 101 | 400 |
| 2 | 337 | 500 | 800 |
| 3 | 337 | 801 | 1200 |
| 4 | 337 | 1500 | 1600 |
| 5 | 337 | 15000 | 16000 |
| 6 | 337 | 20000 | 30000 |
| 7 | 444 | 20 | 30 |
The consumption table data_cons stores multiple batches of consumption for multiple items, with each batch of consumption being an interval.
| ID | ITEM_ID | START_NUM | END_NUM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 337 | 240 | 300 |
| 2 | 337 | 301 | 400 |
| 3 | 337 | 850 | 1100 |
| 4 | 337 | 1500 | 1510 |
| 5 | 337 | 15000 | 16000 |
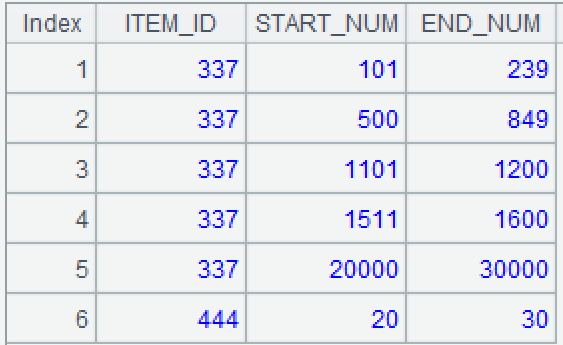
Now we need to calculate the current inventory of each item, which is the difference set between the multi segment range of the original inventory and the multi segment range of consumption, and represent the result as a multi segment range. The interval of the original inventory may be consumed into discontinuous multiple intervals, in which case multiple records need to be naturally generated, with each record corresponding to an interval. For example, the interval of the original inventory [500:1200] is consumed into two intervals [500:849] and [1101:1200].
| ITEM_ID | START_NUM | END_NUM |
|---|---|---|
| 337 | 101 | 239 |
| 337 | 500 | 849 |
| 337 | 1101 | 1200 |
| 337 | 1511 | 1600 |
| 337 | 20000 | 30000 |
| 444 | 20 | 30 |
SQL cannot represent sets with variables, making it inconvenient to perform operations between sets, and the code is very cumbersome. SPL can represent sets with variables, making it easy to express various set operations:
https://try.esproc.com/splx?3xM
| A | B | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | $select * from data_add.txt | $select * from data_cons.txt |
| 2 | =A1.group(ITEM_ID;~.conj(to(START_NUM,END_NUM)):a) | =B1.group(ITEM_ID;~.conj(to(START_NUM,END_NUM)):b) |
| 3 | =A2.join(ITEM_ID,B2,b) | |
| 4 | =A3.derive([a, b].merge@d().group@i( |
|
| 5 | =A4.news(diff; ITEM_ID, ~1:START_NUM, ~.m(-1):END_NUM) |
A1-B1: Load data.
A2: Use the group function to group the original inventory by item, but do not aggregate. Convert each interval within the group into a small set of continuous sequence, and then union them into a large set. ~ represents the current group, the function 'to' can generate a continuous sequence based on the start and end numbers.
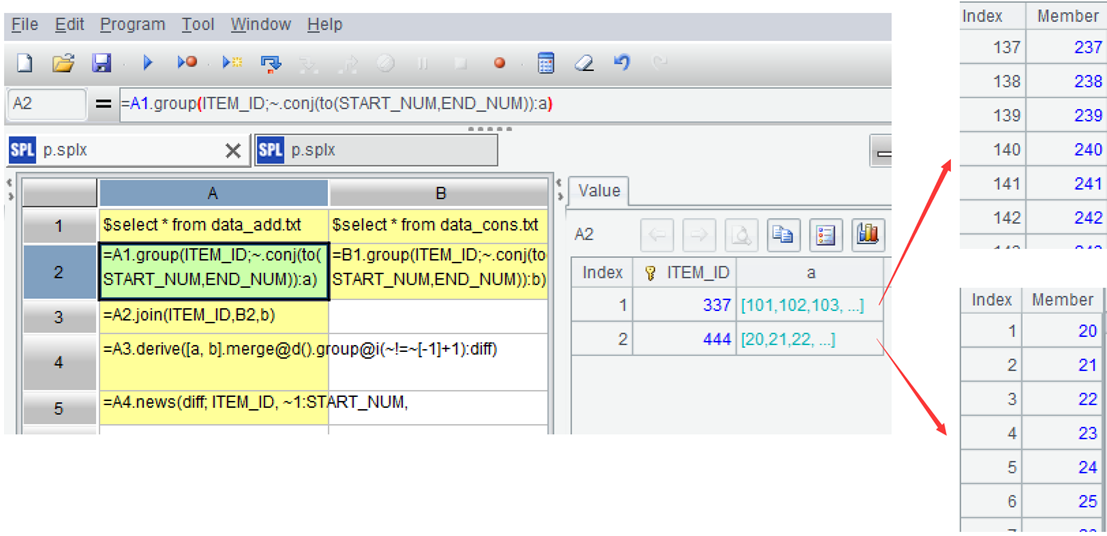
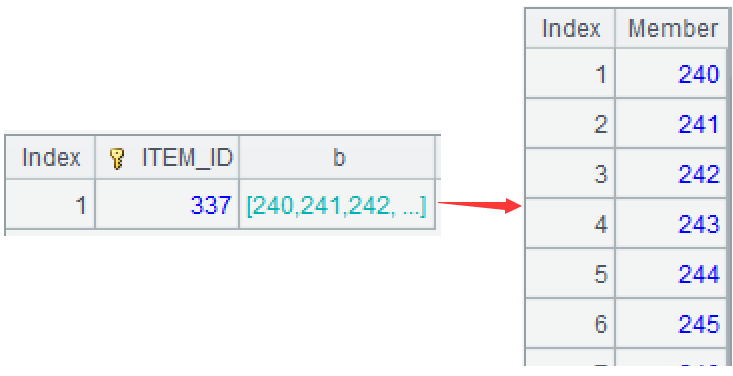
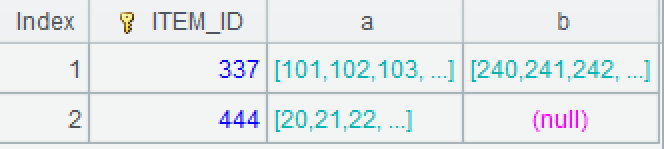
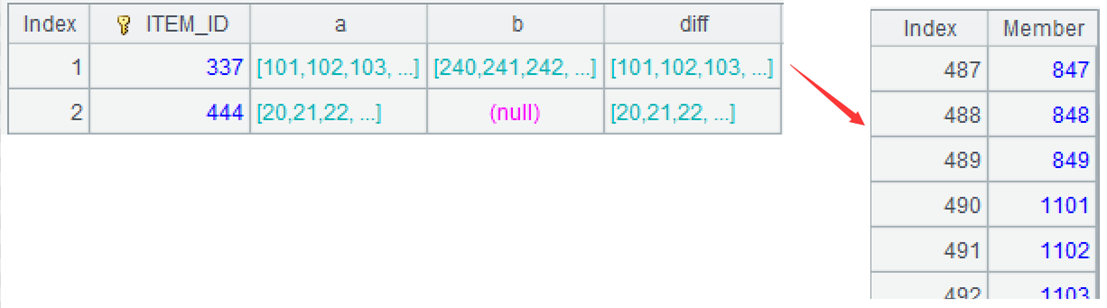
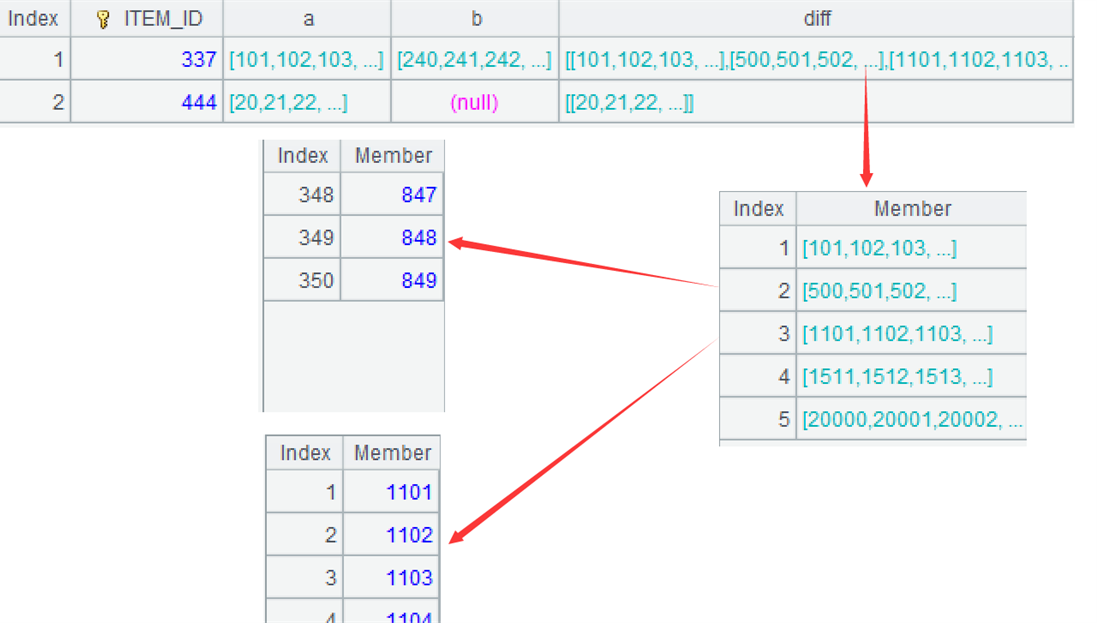
!=[-1]+1) Then perform conditional grouping to each difference set, grouping the consecutive sequence into the same group, such as 849 and 1101 being assigned to the second and third groups, respectively. The function group is used for grouping, by default is equivalence grouping, @i represents grouping by condition, and ~[-1] represents the previous member.
SPL Resource: SPL Official Website | SPL Blog | Download esProc SPL | SPL Source Code