-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 359
How to simplify MongoDB queries with esProc
The native query syntax of MongoDB is quite cumbersome, and simple tasks require long code. Complex calculations are even more difficult to implement, such as:
SPL assists MongoDB: Only keep the running total for the last item in the partition
SPL assists MongoDB: Replace substring in array of objects with nested objects
SPL assists MongoDB: Find multiple latest by filter criteria
esProc provides a MongoDB API with built-in powerful calculation functions that simplify MongoDB queries.
Next, let's try how to integrate esProc into an application.
Download and install esProc first, recommend standard version:
https://www.esproc.com/download-esproc/
| A | |
|---|---|
| 1 | =mongo_open("mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/local") |
| 2 | =mongo_shell@d(A1, "{'find':'grp_score','projection':{'_id':0}}") |
| 3 | =mongo_close(A1) |
Press ctrl-F9 to execute, and you can see the execution result of A2 on the right side of the IDE, presented in the form of a data table, which is very convenient for debugging SPL code.
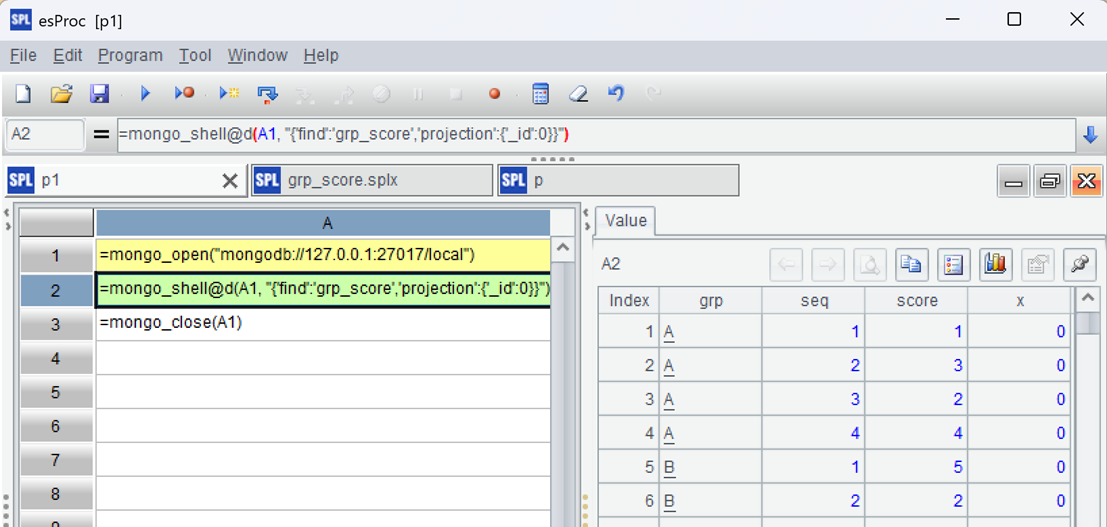
| A | |
|---|---|
| 1 | =mongo_open("mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/local") |
| 2 | =mongo_shell@d(A1, "{'find':'grp_score','projection':{'_id':0}}") |
| 3 | =mongo_close(A1) |
| 4 | =A2.select(seq>=arg1 && seq<=arg2) |
| 5 | =A4.group(grp;(a=~.sort(seq),a.m(-1).x=a.sum(score))) |
| 6 | =json(A4) |
Filter the data through parameters first, and then write the aggregation value on the last record of this group. After running, you can see the result:
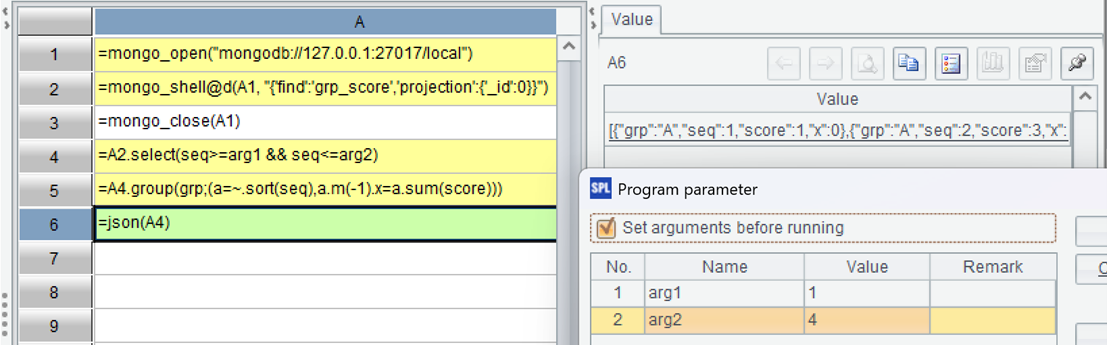
Example 1 above is single-layer data, and Example 2 below is multi-layer data:
| A | |
|---|---|
| 1 | =mongo_open("mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/local") |
| 2 | =mongo_shell@d(A1, "{'find':'meetings','projection':{'_id':0}}") |
| 3 | =mongo_close(A1) |
| 4 | =A2.run(organizer.run(avatar="https://new.com/"+mid(avatar,17)), meetings.run(owner.run(avatar="https://new.com/"+mid(avatar,17)), participants.run(avatar="https://new.com/"+mid(avatar,17)) ) ) |
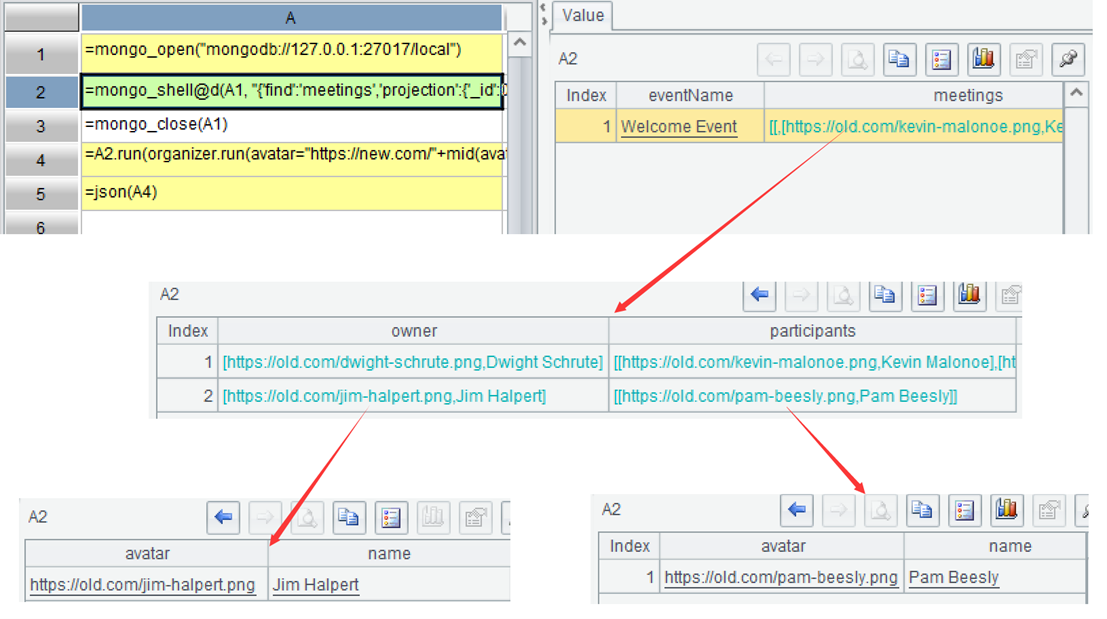
On the right side of the IDE, you can expand and observe multiple layers of data layer by layer, where the structure of A2 is as follows:
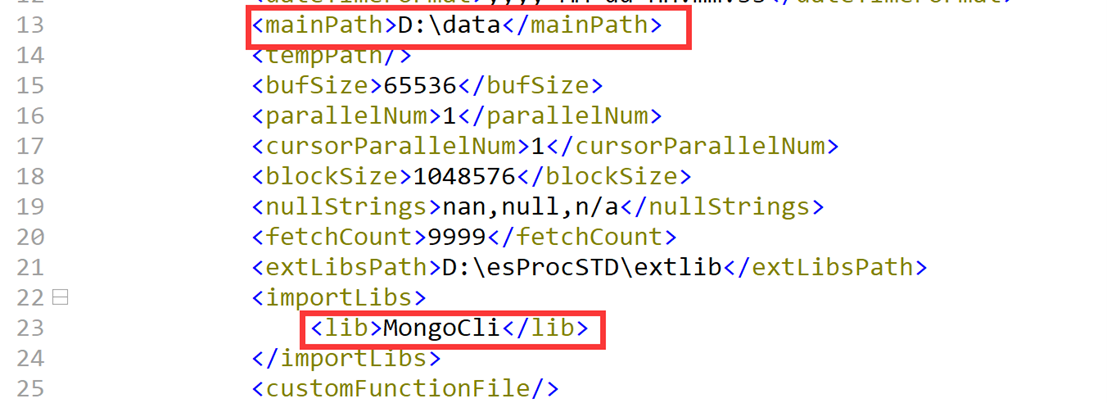
Deploy these two jars to the class path of the Java development environment. The jars of external libraries will be dynamically loaded through configuration files and do not require manual deployment. Find the esProc configuration file raqsoftConfig.xml from the directory "[Installation directory]\esProc\config" and deploy it to the Java development environment's class path.
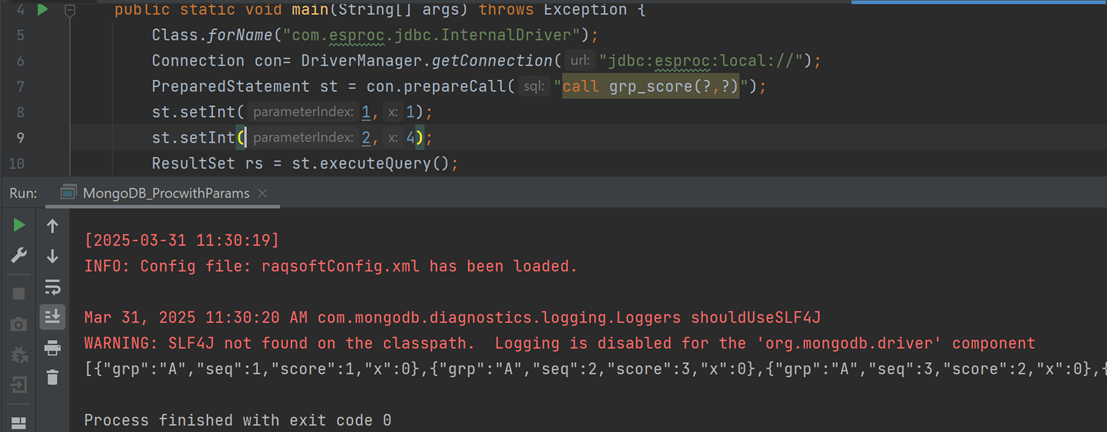
Class.forName("com.esproc.jdbc.InternalDriver");
Connection con= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:esproc:local://");
PreparedStatement st = con.prepareCall("call grp_score(?,?)");
st.setInt(1,1);
st.setInt(2,4);
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery();
After running, you can see the result:
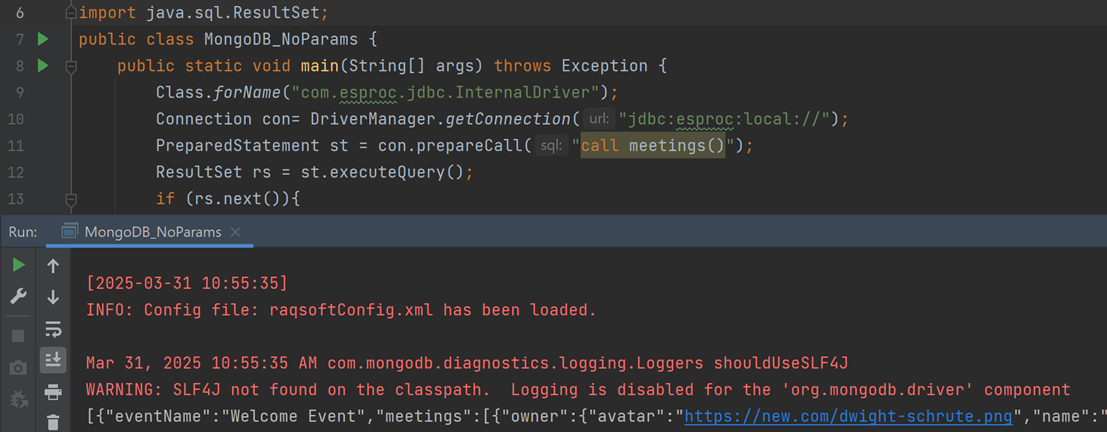
Class.forName("com.esproc.jdbc.InternalDriver");
Connection con= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:esproc:local://");
PreparedStatement st = con.prepareCall("call meetings()");
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery();
The execution result looks like the following:
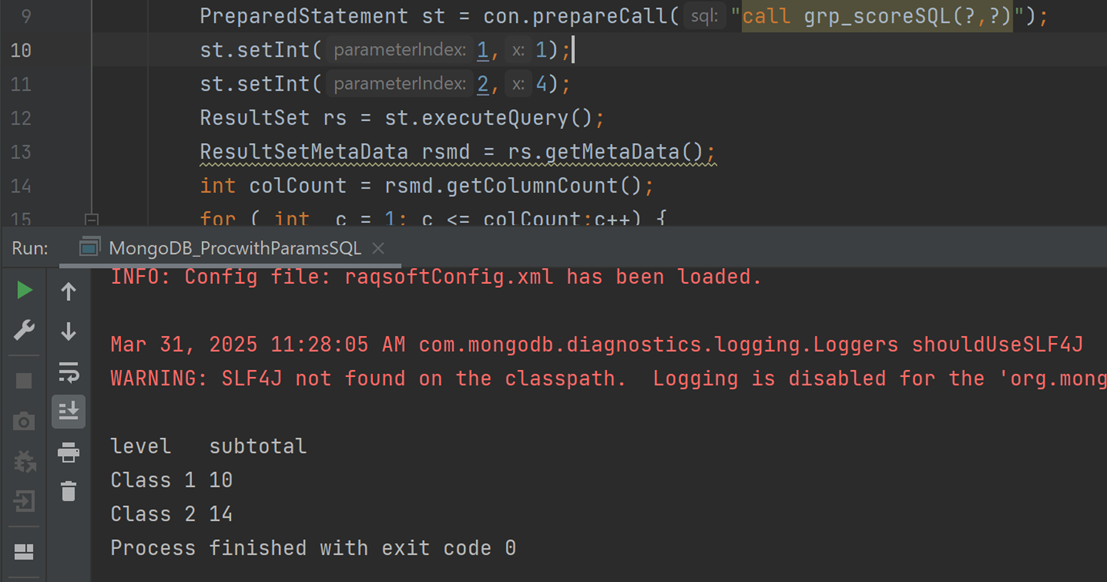
| A | |
|---|---|
| 1 | =mongo_open("mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/local") |
| 2 | =mongo_shell@d(A1, "{'find':'grp_score','projection':{'_id':0}}") |
| 3 | =mongo_close(A1) |
| 4 | $select case grp when 'A' then 'Class 1' when 'B' then 'Class 2' else 'others' end level,sum(score) as subtotal from {A2} where seq>=? and seq<=? group by grp ;arg1,arg2 |
| 5 | return A4 |
Save the script file as grp_scoreSQL.splx, and the result after execution is as follows:
SPL Resource: SPL Official Website | SPL Blog | Download esProc SPL | SPL Source Code